| Feature |
Sample Screen
|
Explanation
|
Display an Interactive
Sky Chart |
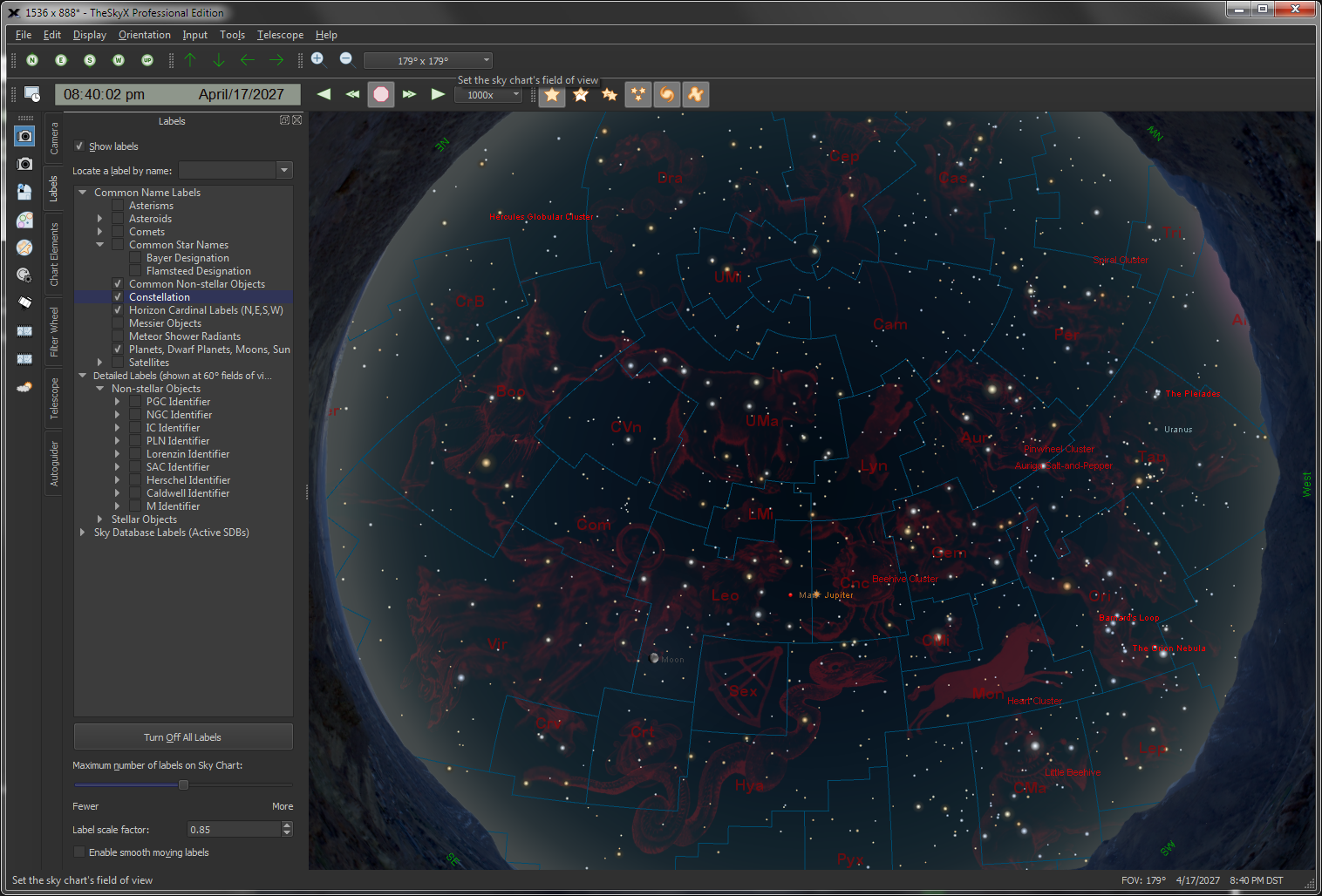
Looking up at dusk.

Looking North.
|
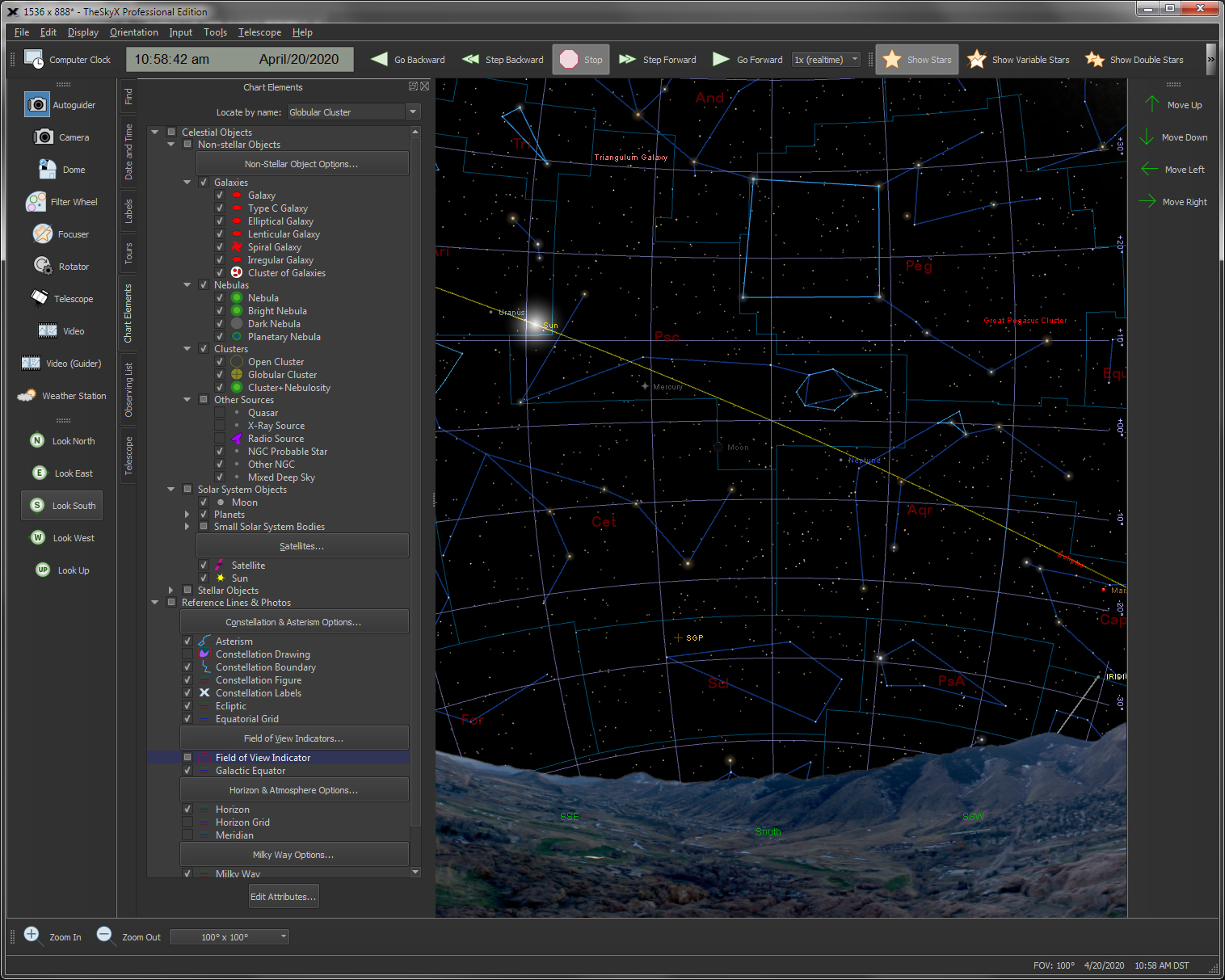
The flexible and interactive Sky Chart shows you the simulated sky.
-
Input any date from 4,712 B.C. to A.D. 10,000 and any time of day to show the simulated star chart for your location.
-
Click the North, South, East, West or Look Up buttons to orient the chart
as it would appear from your backyard.
-
Change the magnification to show any field of view, from 235°
down to 30 arc seconds across.
|
Databases of Celestial Objects
and Photos |
Large databases of pictures and
photos.
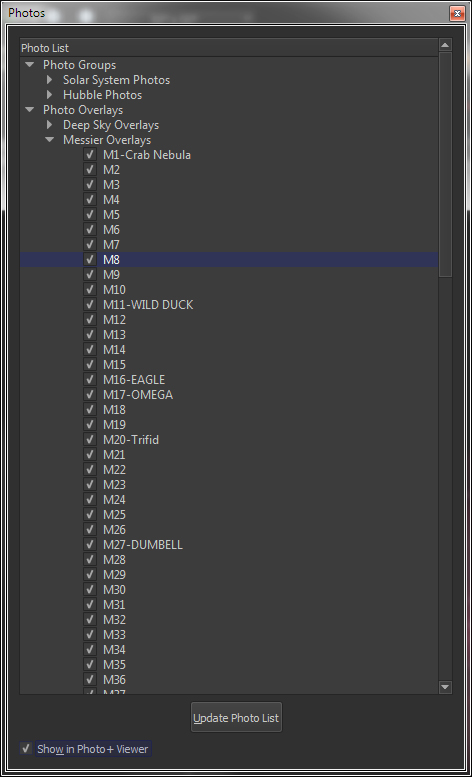
Photos tab
|
TheSky Serious is packed with information on millions of objects and thousands of fascinating astronomical photographs.
View and find the planets, dwarf planets, the Moon, comets, asteroids, satellites, and thousands of the most popular non-stellar objects from the Messier, NGC and IC catalogs and approximately 1 million stars from the Hipparcos-Tycho star catalog (complete to about 12th magnitude).
Databases of Objects and Photos
|
Solar System
|
- Sun
- Mercury
- Venus
- Earth (in 3D Solar System)
- Earth’s Moon
- The Moon
- Mars
- Mars’ Moons
- Io
- Europa
- Ganamede
- Callisto
- Jupiter
- Jupiter’s Moons
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Neptune
- Pluto
- Comets (up
to 1100 at a time)
- Asteroids (just shy of 1 million)
- Satellites (up to 10,000)
|
|
Non-Stellar Objects
|
- 7,431 objects from the New General Catalog (NGC)
- Index Catalog (IC)
|
|
Stars
|
- Hipparcos/Tycho Catalog, 1.2 million stars
|
TheSky also includes:
-
Over 13,000 images from the
NGC and IC Catalogs.
-
Photos of every object in
the Messier catalog.
-
Photos of solar system objects,
including images from the Mars Rover and other space missions.
-
Over 1000 high-resolution
photographs of the moon.
|
|
Show
What’s Up Tonight
|

What’s
Up? Report
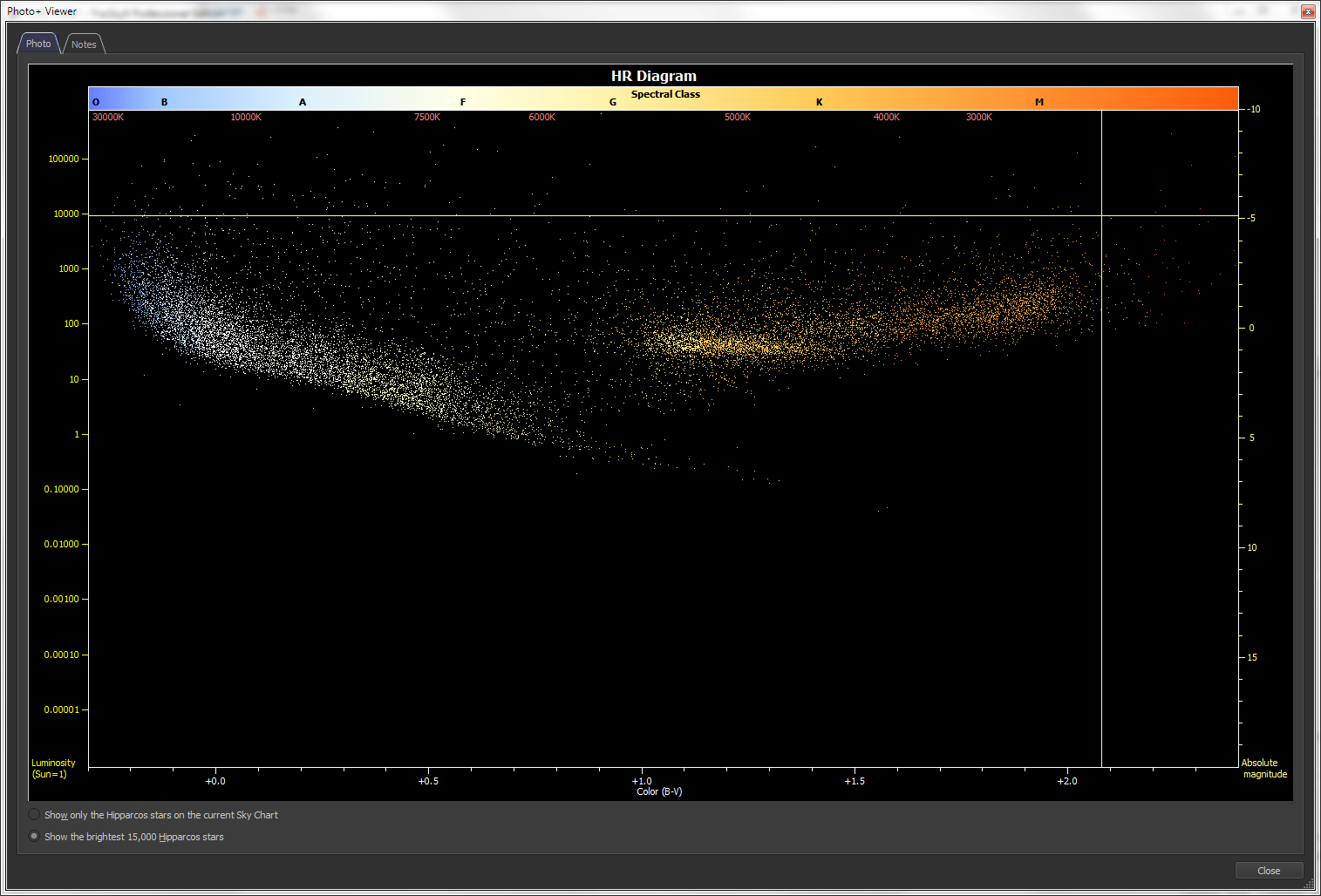
Hertzsprung-Russell
diagram
Wide-field
chart showing the location of Saturn tonight.
|
The simplified observing list includes a What’s Up? query that lets you specify the viewing time, your optical aid (naked eye, binocular, or small telescope) and which objects you’re interested in seeing tonight; TheSky’s What Up? command generates a report for you, complete with fascinating descriptions about many deep-space objects, sample photographs of the object (when available), and Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagrams for stars.
You can scroll through each object in the report and watch the Sky Chart update to show you exactly where to look for the object.
|
|
Create and Show Field of View Indicators (FOVIs)
|
FOVI
around the Horsehead nebula
|
Choose your equipment from a database of hundreds of telescopes, eyepieces and cameras or define your own, then show an overlay on the Sky Chart.
|
|
Predict
and Watch Iridium Flares
|
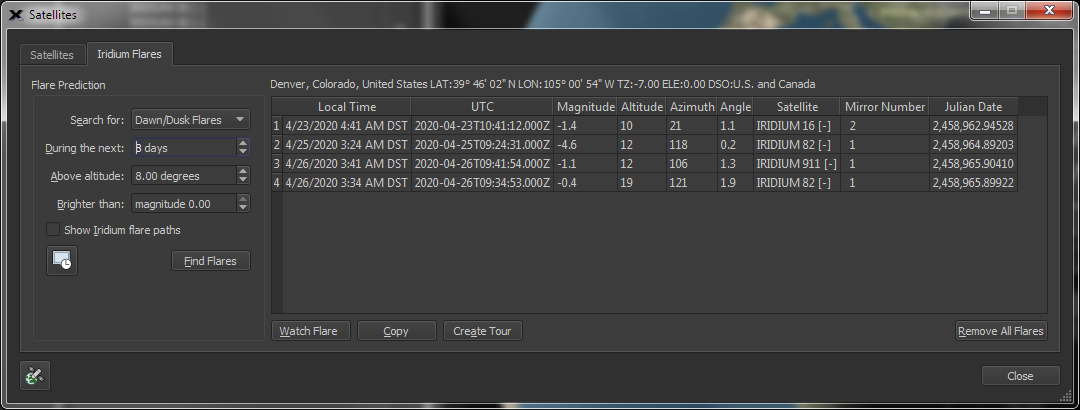
Iridium
Flare Report
|
Predict and watch simulated Iridium Flares directly from TheSky.
|
|
Watch
Animated Tours
|
Tour
showing the Sun’s analemma
|
TheSky includes animated tours that you can watch, learn, or show others basic astronomy concepts.
Supplied Tours include:
-
Sun’s Analemma
-
Angular Size of Mars
-
Equatorial Coordinates
-
Horizon Coordinates
-
Mercury Evening
Visibility
-
Mercury Morning
Visibility
-
Moon Cycle – Size and Phase
-
Motion of Barnard’s Star
-
24-Hour Motion of Saturn’s Moons
-
Rotation and Phase of Mercury 2008
-
Rotation and Phase of Venus 2008
-
10-yeaar View of Saturn from Earth
-
Venus and Mercury Annual Paths
-
What was that? Iridium Flare Sample
-
Winter Constellations
|
| Configurable Windows |
Tabbed windows on the Sky Chart.
|
By default, commonly used features can be accessed by clicking the appropriate tab on the left side of the Sky Chart.
List of the standard docking windows:
Tours window – Watch animations related to many interesting astronomical concepts.
Find window – Easily locate any object by name, catalog number and many other designations.
Chart Elements window – Lets you turn on and off, or filter by
upper and lower magnitude or angular size, elements on the Sky
Chart, including:
-
-
Non-stellar objects (Type C, elliptical, lenticular, spiral, irregular galaxies and clusters of galaxies; bright, dark and planetary nebulas; open and globular clusters and clusters plus nebulosity; probable NGC stars, other NGC objects)
-
Solar system objects (the Moon, planets, small solar system objects including Pluto, comets and asteroids, the Sun, and planets’ moons) and satellites.
-
Stellar objects (stars, double stars, suspected variables and variables).
-
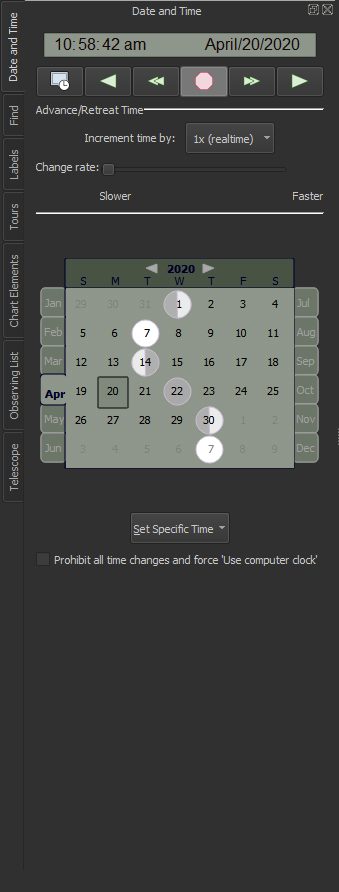
Date & Time window – Includes controls to specify the current date and time, including a calendar control showing the phases of the moon, a context menu button to set specific times (now, sunrise, noon, sunset, midnight, morning, new moon, first quarter, last quarter, full moon, moonrise, moonset, vernal (spring) equinox, summer solstice, autumnal equinox, winter solstice or any Julian date), advance/retreat time controls and more.
Labels window – Turn on and off the names of objects, including:
- asterisms
- asteroids
- comets
- common non-stellar
objects
- direction markers
(NSEW)
- Messier objects
- meteor shower
radiants
- planets, dwarf
planets, the moon, planets’ moons, and the sun
- stars, including the Bayer designation, Flamsteed designation, and common names
Photos window – Show color or black and white photographs for thousands of deep-sky objects.
These windows appear by default as a tab and represents an independent window that can also be undocked, moved and sized to your liking.
|
|
Find Objects
|
Simple
Find
A list of common names that match the letters you type appears automatically.
Advanced tab
All object in TheSky’s
databases can be found in the Advanced list.
|
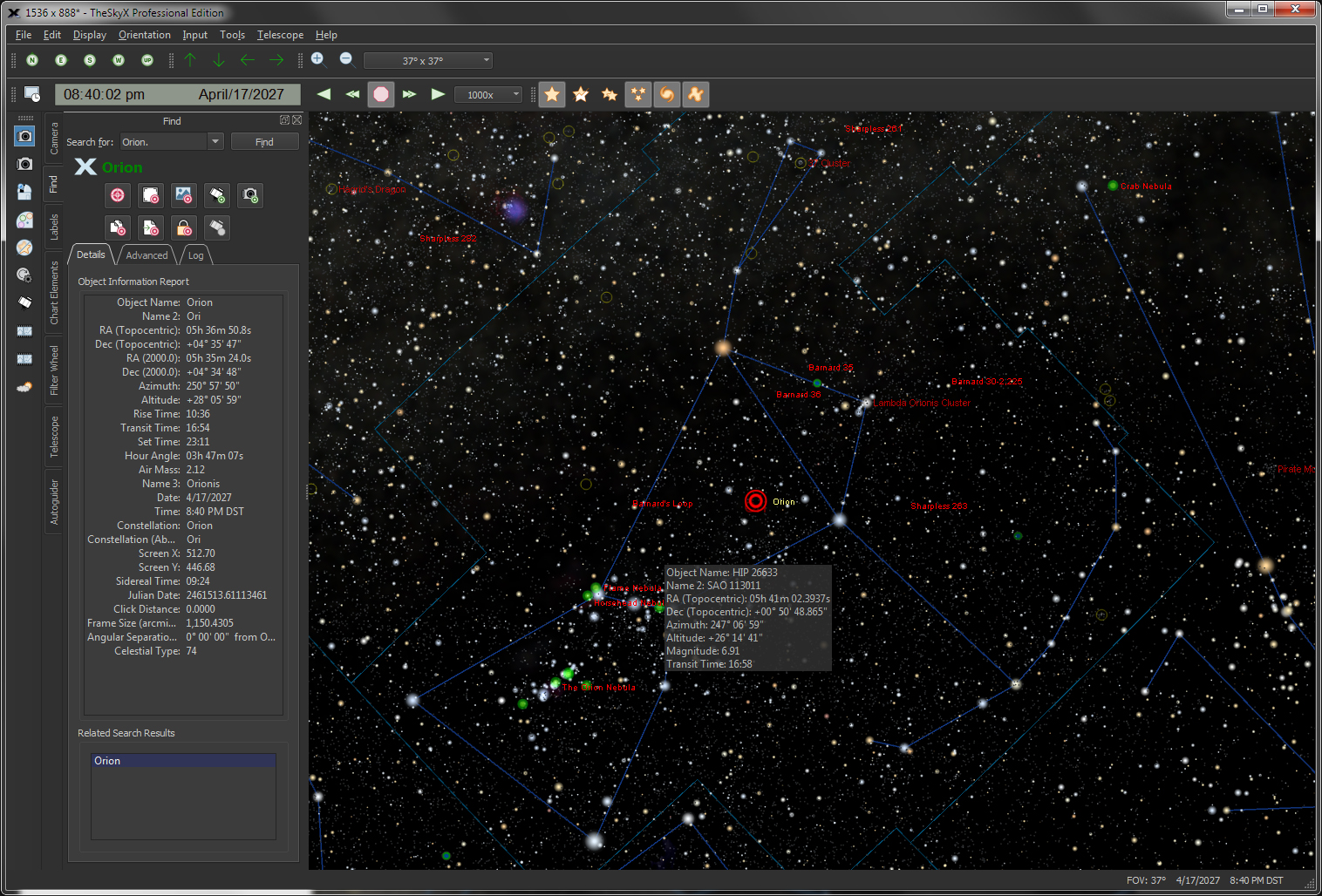
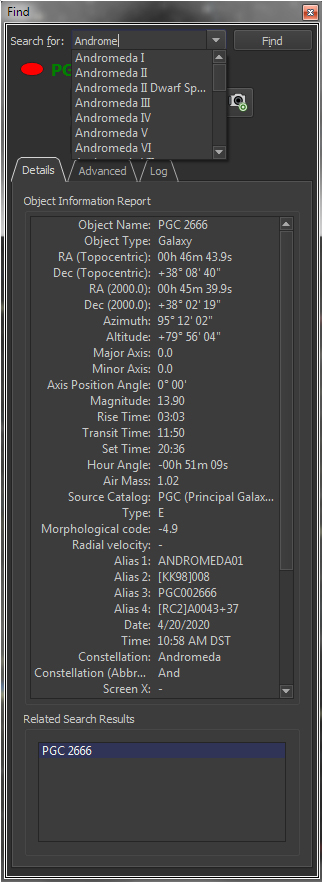
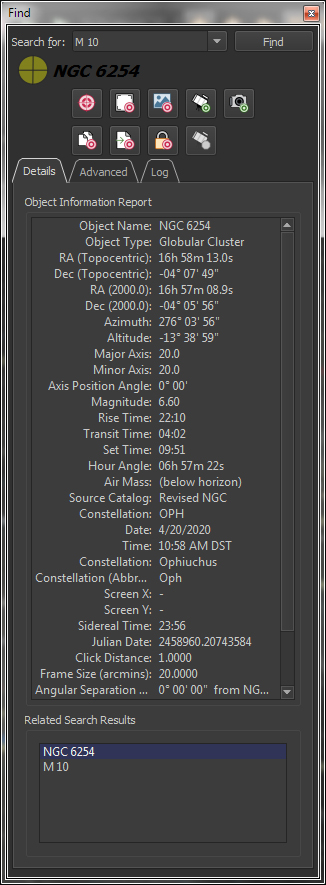
The friendly, powerful Find command lets you easily locate any object in TheSkyX’s astronomical databases.All objects in the databases are listed in a “tree list” and sorted by type (star, double star, galaxy, cluster, etc.). Just double-click on the name to find it, or specific classification, including…
Finding Stars by:
-
- Common name (a list of common names that match the
letters you type appears automatically)
- Bayer designation
- Flamsteed designation
- General Catalog of Variable Star (GCVS) designation
- Non-stellar variable star (NSV) designation
- Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) Catalog
number
- Struve designation
- Washington Catalog of Double Star designation
Finding Non-stellar objects by:
-
- Caldwell number
- Common name
- Herschel number
- Index Catalog number (IC)
- Lorenzin Catalog number
- New General Catalog (NGC/IC Project) number
- Principle Galaxy Catalog number (PGC)
- Principle Galaxy Catalog cross-reference number
- Zwicky designation
- Arakelian Catalog of Galaxies designation
- Catalog of Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies (CGCG)
designation
- David Dunlop Observatory Catalog of Galaxies designation
- Fairall Catalog of Galaxies designation
- Karachentseva Catalog of Galaxies designation
- Kazaryan UV Galaxies designation
- Kiso UV Galaxies designation
- Second Byurakay Survey designation
- Tololo Galaxies designation
- Uppsala General Catalog of Galaxies (UGC)designation
- University of Michigan Catalog of Galaxies designation
- Virgo Cluster Catalog of Galaxies designation
- Weinberger Catalog of Galaxies designation
- Planetary Nebula designation (PLN)
- Saguaro Astronomy Club Deep-Space Object catalog
(SAC)
Finding Solar System Objects:
-
- Comet’s by name
- Asteriod by name or number
- Moon
- Satellites
- Sun
- Mercury
- Venus
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Neptune
- Pluto
Finding the Constellations by:
Find 70 Common Asterisms
The object’s name appear in green letter if it’s currently above the horizon, or in black italicized letters when it’s below the horizon.
|
Get Detailed Information on Celestial
Objects |

Object
Information reports are configurable to show as much, or as little
information as you need.
|
Click on any object, or use the Find command to show extensive information on celestial objects, including…
-
- Object type (star, cluster, galaxy, nebula, etc.)
- Right ascension and declination coordinates (current)
- Right ascension and declination coordinates (Epoch
2000)
- Altitude and azimuth coordinates
- Object magnitude*
- Common name*
- Catalog number (including cross references to other
catalogs), for example M42 or NGC 1976v.*
- Description of the object*
- Visual magnitude*
- B magnitude*
- V magnitude *
- Parallax*
- Proper motion*
- Sidereal time
- Distance from Earth (in light years or parsecs)*
- Rise, transit, set times
- The constellation to which the object belongs
- Equatorial and horizon-based coordinates
- Other object and catalog specific data
- Position angle (as measured from the celestial pole)
from the previously identified object
- Phase or percent illumination*
- Air mass
*Note that not every database or every object in a particular database used by TheSky contains information about every parameter listed above. For example, most astronomical catalogs do not contain an object’s distance to Earth information. Good news: the Gaia star catalog does contain star distance from Earth for every star!
Sample Object Information
The table below lists the typical information displayed for different classifications of objects.
| Object Type |
Information |
|
Stars
|
Polaris
SAO 308
GSC 4628:237, HIP 11767, PPM 431, HD 8890, B+88 8
Flamsteed-Bayer: 1-Alpha Ursae Minoris
Spectral: F7:Ib-IIv SB** Data from Hipparcos Catalog****Proper motion (mas/yr): RA = 44.22, Dec = -11.74
Magnitudes Bt: 2.756, Vt: 2.067
Parallax: 7.560 mas, 132.2751 pc
Distance: 431.42 light-years, 27283753.74 astronomical units
Magnitude: 1.97
RA: 02h 34m 10.632s Dec: +89°15’58.530″
RA: 02h 31m 49.084s Dec: +89°15’50.794″ (Epoch 2000)
Azm: 359°35’34” Alt: +39°05’34”
Always above horizon. Transit: 05:40
Hour angle: 10h 16m 39.2s Air mass: 1.59
Position error: 0.60 mas |
|
Deep-space
objects
|
Great Nebula in Orion
Orion Nebula
M42
NGC 1976
Other description: Nebula.
Constellation: Ori
Dreyer description: A magnificent (or otherwise interesting)
object! Theta1 Ori and the great nebula; = M42.
Magnitude: 4.0
RA: 05h 35m 27.3s Dec: -05°26’49”
RA: 05h 35m 24.0s Dec: -05°27’00” (Epoch 2000)
Azm: 279°11’58” Alt: -19°16’00”
Rise: 02:56 Transit: 08:40 Set: 14:24
Size:66.0′
Hour angle: 07h 22m 24.6s
From Polaris:
Angular separation: 94°56’15”
Position angle: +134°09′ |
|
Comets,
Minor Planets, Satellites
|
Satellite: OKEAN 3 (#21397U)
Latitude: 61°15’15” Longitude: 98°01’11”
Height: 633.92
Range: 2623.0 Range Rate: 6.8134.
Phase angle: 68.4
Rates ra: 110.0274 dec:-223.6962 (arcsecs/sec)
RA: 23h 47m 16.6s Dec: +52°14’26”
RA: 23h 47m 11.7s Dec: +52°13’53” (Epoch 2000)
Azm: 09°18’05” Alt: +02°56’44”
Rise: 00:00 Transit: 00:00 Set: 00:00
Hour angle: -10h 58m 58.2s Air mass: 15.25
From Eltanin:
Angular separation: 50°38’20”
Position angle: +52°20′ |
|
Planets,
Sun, Moon
|
Jupiter
Rise: 2:14 AM on 8/20/2001
Transit: 9:39 AM on 8/20/2001
Set: 5:04 PM on 8/20/2001
RA: 06h 34m 48.4s Dec: +22°58’12”
Azm: 291°37’52” Alt: +10°00’36” (with refraction:
+10°05’58”)
Phase: 99.426%, Apparent magnitude: -2.06
Heliocentric ecliptical coordinates:
l: 89°19’16.1″ b: -00°15’12.1″ r: 5.122584
Geometric geocentric ecliptical coordinates:
l: +98°01’05” b: -00°13’37” r: 5.715020
Mean geometric ecliptical coordinates:
l: +98°00’56” b: -00°13’38” r: 5.714970
True equatorial coordinates: RA: 06h 34m 49s Dec: +22°58’13”
Physical Data
DE: 2.15°, DS: 2.32°, Position angle: 4.57°.
Longitude of central meridian:
System I: 72.28°, System II: 170.48°
Correction for phase: 0.33
Apparent equatorial diameter: 34.4
Apparent polar diameter: 32.2Rates RA: 0.0083 Dec: -0.0004 (arcsecs/sec) |
|
Select Different Photographs for the
Panoramic Horizon |
Software Bisque Observatory
Mountain horizon
|
Choose from several supplied custom panoramic horizons, including:
- Cayman Island scene
- Desert scene
- Forest scene
- Grand Mesa, Colorado
- Ice Lake, Michigan
- Mountain scene
- Mt. Wilson Institute Observatory
- New Mexico Skies
- Software Bisque Observatory
- Very Large Array
- Winter Star Party
|
Quickly Set Chart Options with Chart
Elements |

Chart
Elements tab
|
Turning on and off individual, selected or all object classifications or “chart elements” is easy with the Chart Elements window.
|
| Show Reference Lines and Photos |
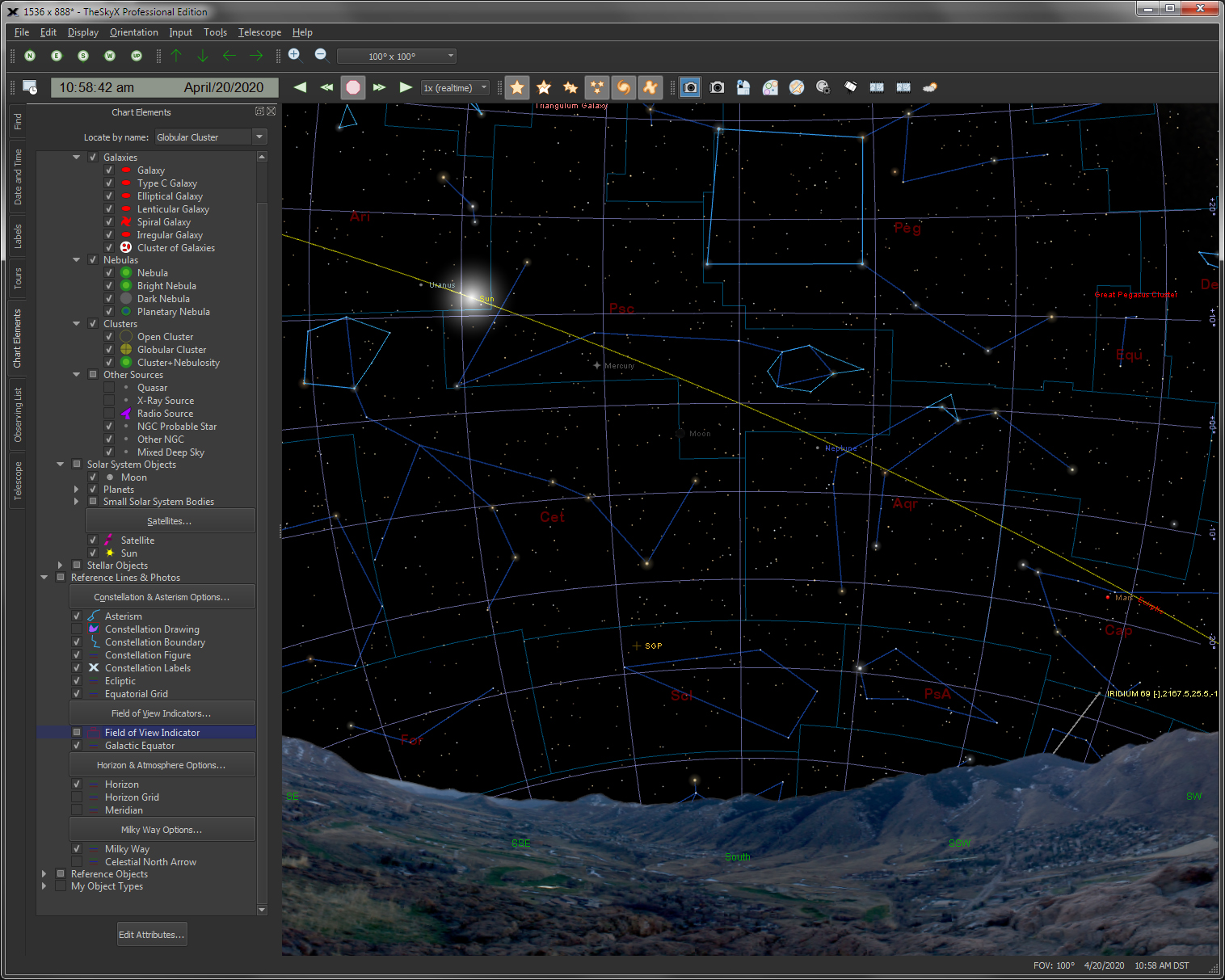
Reference Lines and Reference Photos
|
Show the following reference lines and reference photos.
Constellation Figures from:
- Astronomy Magazine
- H.A. Rey
- Patrick Moore
- Sky & Telescope Magazine
- TheSky/Software Bisque
- Will Tirion
- Milky Way Galaxy (Isophotes,Black & white photo,Full color photo)
- Constellation Boundaries
- 70 popular Asterisms
- Ecliptic line
- Equatorial Grid lines
- Galactic Equator
- Horizon Grid lines
- Meridian
- Celestial North/South Arrow
|
| Show Object Names (Object Labels) |
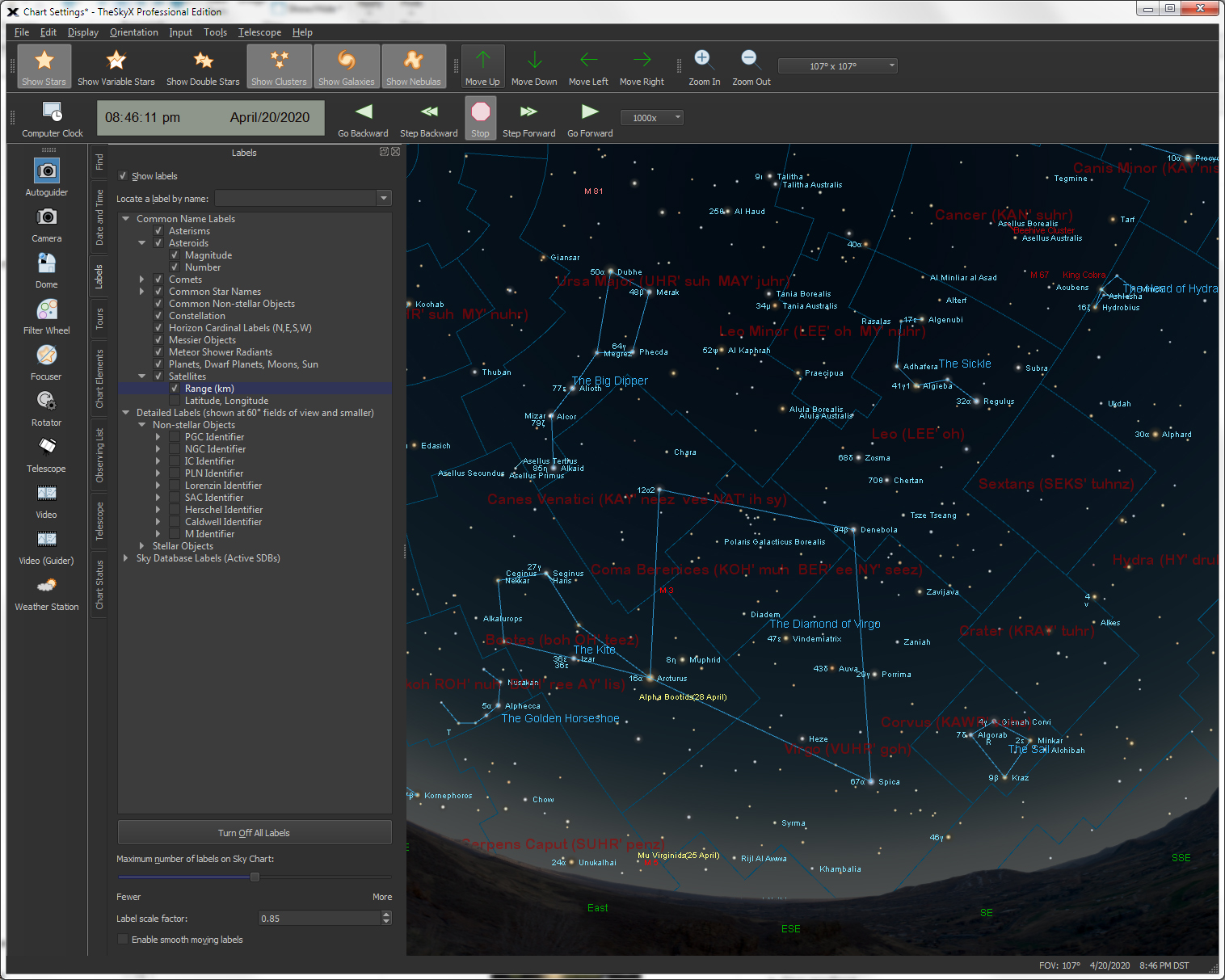
Object Name Labels
|
TheSky can show the names and labels for the following:
- Asterisms
- Asteroids
- Comets
- Common Non-stellar Objects
- Constellations
- Direction Markers (NSEW)
- Messier Objects
- Meteor Shower Radiants
- Planets, Dwarf Planets, Moons,
Sun
- Satellites
- Star Labels (Bayer Designation, Common Star Names, Flamsteed
Designation)
|
| Configure Appearance of Stars |
Sample star field
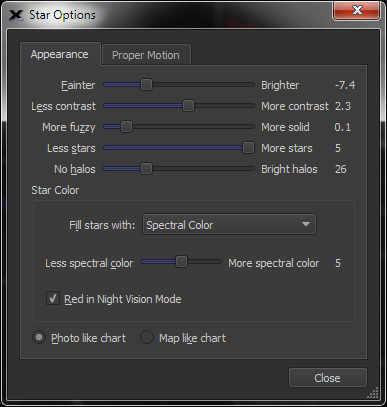
Star Options
|
Adjust the appearance of the stars by:
- Brightness
- Contrast
- Star gradient
- Star density
- Size of surrounding halo
- Spectral color or custom fill
color
- Spectral color saturation
|
Customize Tool bars to Access Commands
You Want |

Look tool bar
Orientation tool bar
Tool bars positioned around the Star Chart
|
Six standard tool bars contain buttons to access many frequently used commands.
You can also add your own custom tool bars for the commands you
use most. The size of the buttons on the tool bars are configurable, as well as the content of the buttons (show
a graph, or text or both on the button).
The position of the tool bars can be customized. Show them as floating windows, or drag and drop them anywhere along the edges Star Chart window.
|
| Chart Status window |
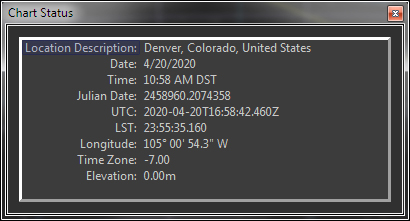
Chart Status window with configurable report
|
The Chart Status window shows a continuously updated information about the current chart. Choose from the following list of status report options:
- Date
- Time
- Julian Date
- Universal Time (UT)
- Local Sidereal Time (LST)
- Location Description
- Latitude
- Longitude
- Time Zone
- Elevation
- Screen Center Right
Ascension (RA)
- Screen Center Declination (Dec)
- Screen Center Right
Azimuth (Az)
- Screen Center Altitude (Alt)
- Screen Field Width
- Screen Rotation
- Cursor X position
- Cursor Y position
- Cusor Constellation
- Cursor Right Ascension/Declination (RA/Dec)
- Cursor Azimuth/Altitude
(Azm/Alt)
|
| Show/Hide Scroll Bars |

Chart with optional scroll bars turned on
|
Show/hide horizontal and vertical scroll bars for easy chart navigation.
|
| Look North, South, East, West or Up |
   

|
Never get lost in space!
Automatically adjust the star chart for your location to look North, South, East, West or straight up (at the Zenith).
|
| Zoom Box |
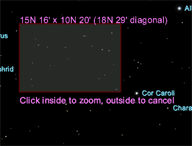
Zoom Box
|
Click and drag the “zoom box” on the chart to magnify (or
zoom in) to this region. The size (or field width) and the
angular separation between the corners of the zoom box is shown.
|
| Zoom to Pre-defined Fields of View |
 |
Minimum
(30 arcseconds)
|
 |
Telescope
(1°)
|
 |
Finder
(10°)
|
 |
Binocular
(50°)
|
 |
Wide Field
(180°)
|
 |
Maximum
(235°)
|
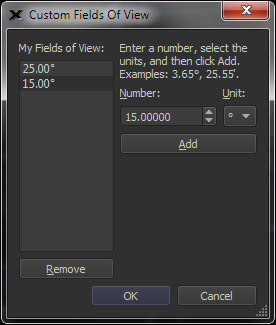
Custom Field of View window.
|
Built-in command to show the following fields of view:
-
Minimum (30 arcseconds)
-
Telescope (1°)
-
Finder (10°)
-
Binocular (50°)
-
Naked Eye (100°)
-
Wide Field (180°)
-
Maximum (235°)
Or, define any number of custom fields of view using the Custom Fields of View dialog.
|
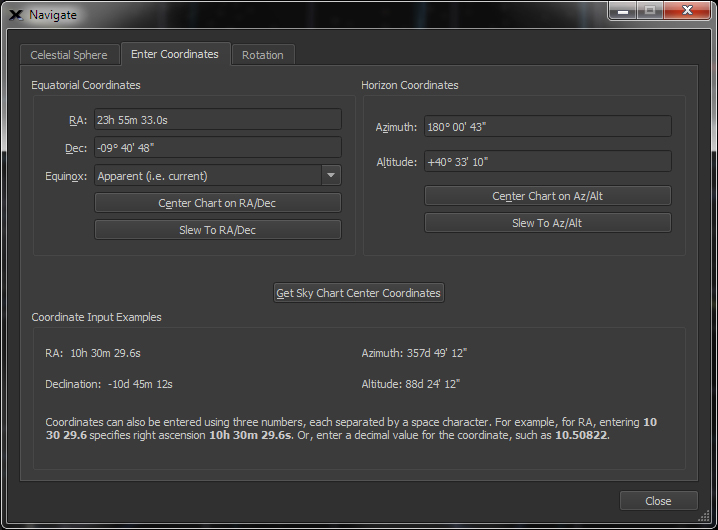
| Navigate the Celestial Sphere |
|














































