TheSky Features
TheSky Professional, on macOS, Windows, Linux ARM64, ARM32, and x86_64 architectures, is your astronomy toolkit and is loaded with features you need. The table below lists most of TheSky Professional’s standard feature set. In addition to these standard features, TheSky Professional offers optional modules that extend the standard feature set.
Which edition is right for you?
Planetarium and Charting Features
|
Sample Screen |
Explanation |
|||||||||||||
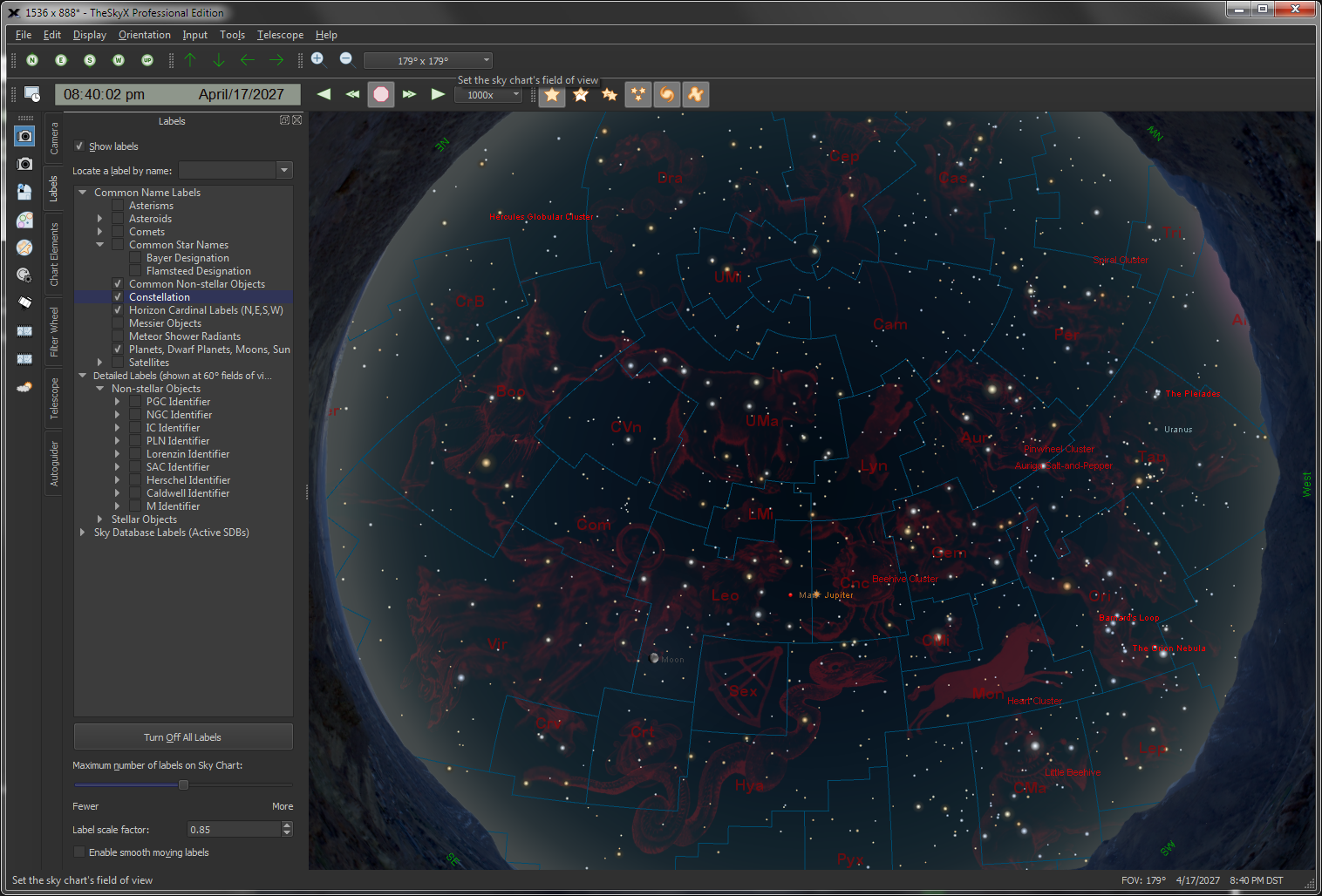
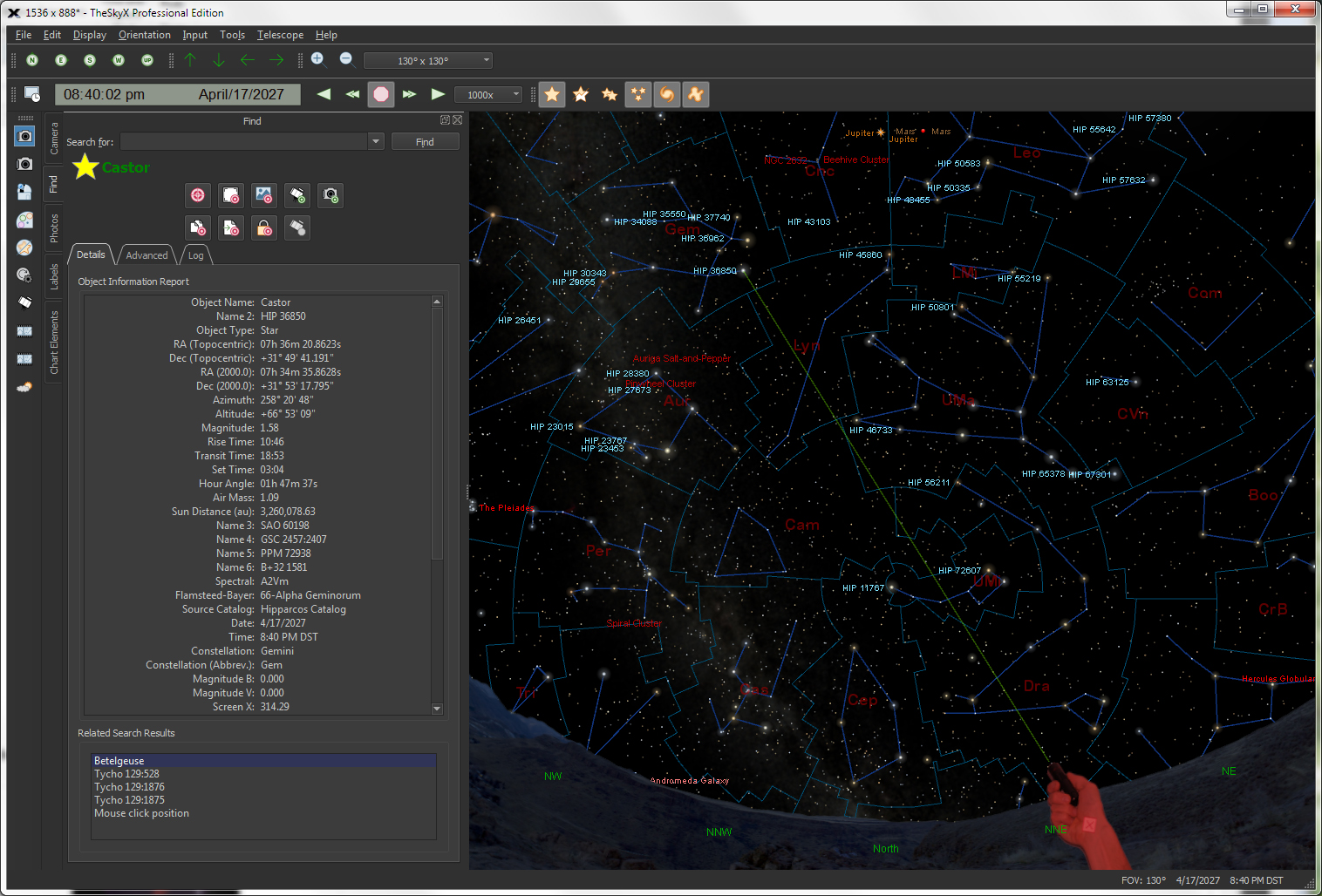
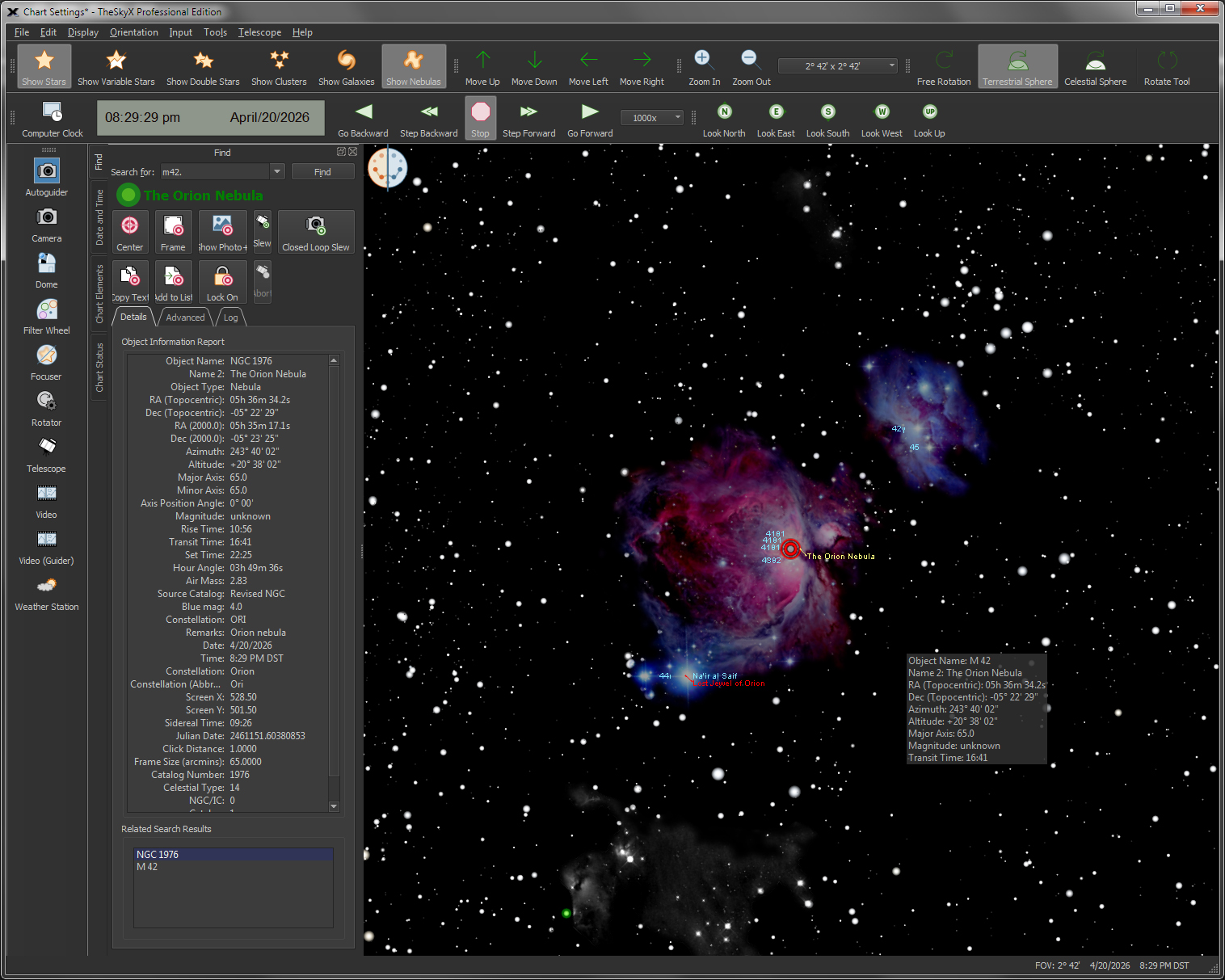
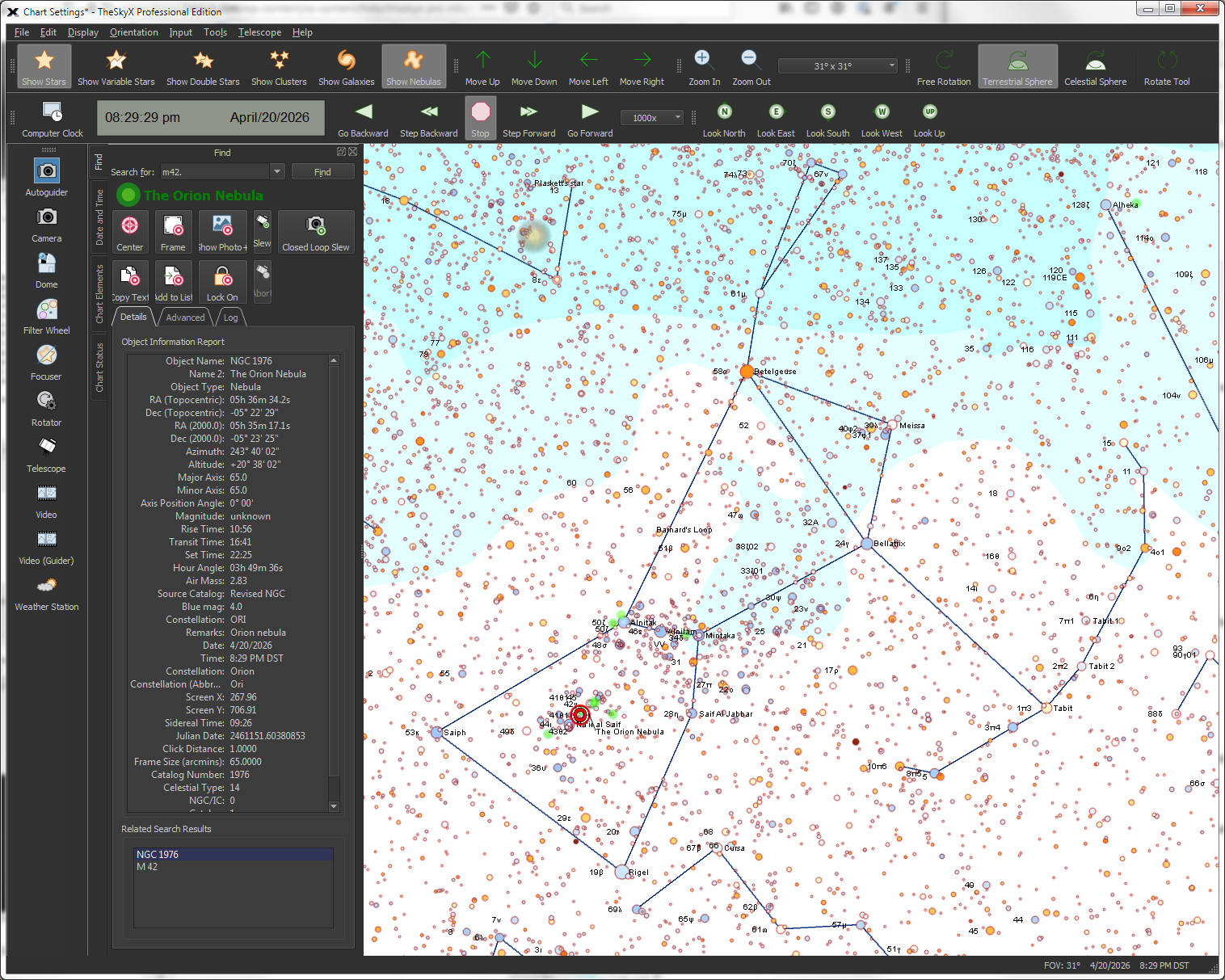
| Display an Interactive Sky Chart |
Looking up at dusk.
Looking North.
|
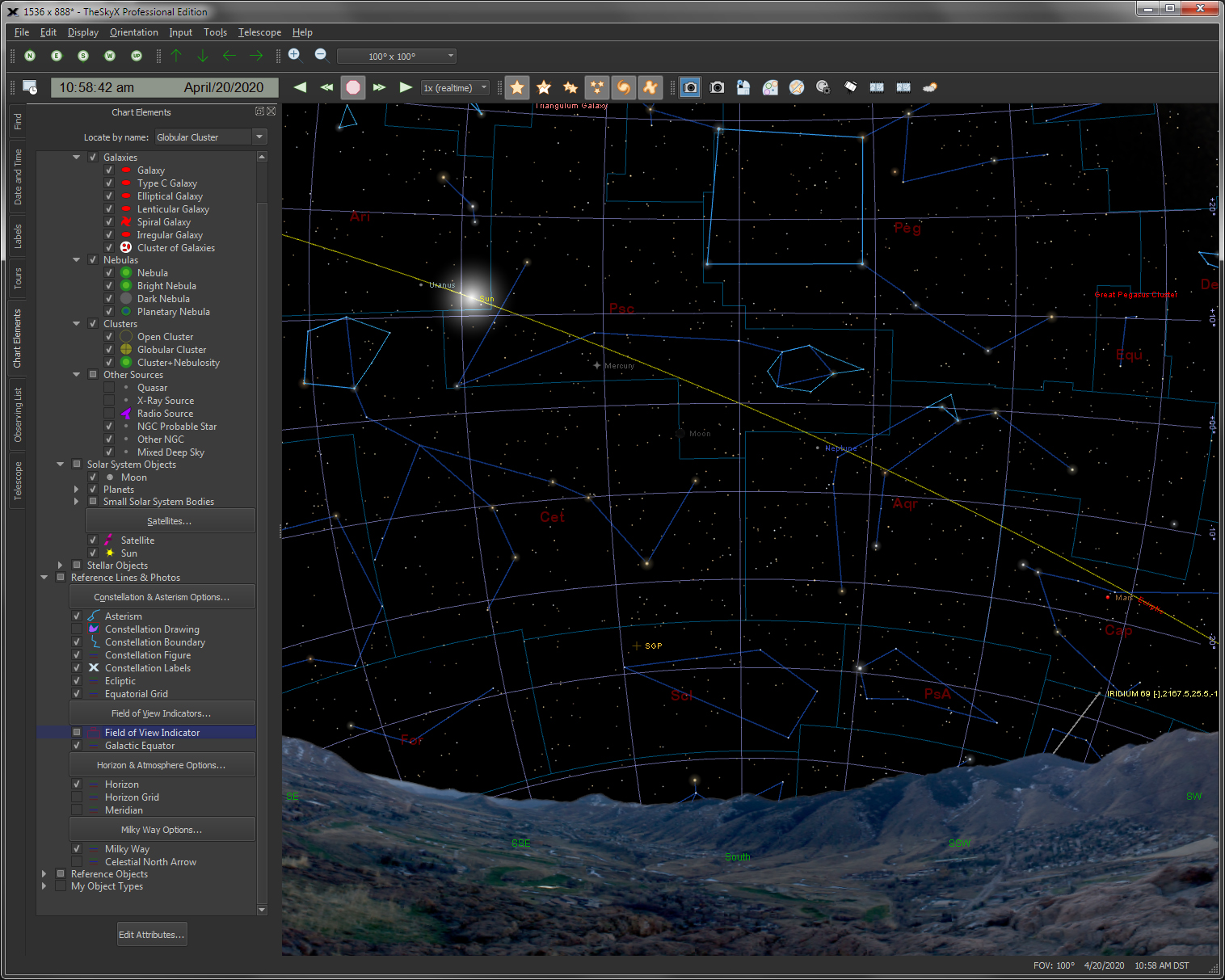
The flexible interactive Sky Chart shows you the simulated sky.
|
||||||||||||
| Databases of Celestial Objects and Photos |
Large databases of pictures and
Photos tab
|
TheSky is packed with information on millions of objects and thousands of fascinating astronomical photographs. View and find the planets, dwarf planets, the Moon, comets, asteroids, satellites, and thousands of the most popular non-stellar objects from the Messier, NGC and IC catalogs and approximately 1 million stars from the Hipparcos-Tycho star catalog (complete to about 12th magnitude). Databases of Objects and Photos
TheSky also includes:
|
||||||||||||
|
What's
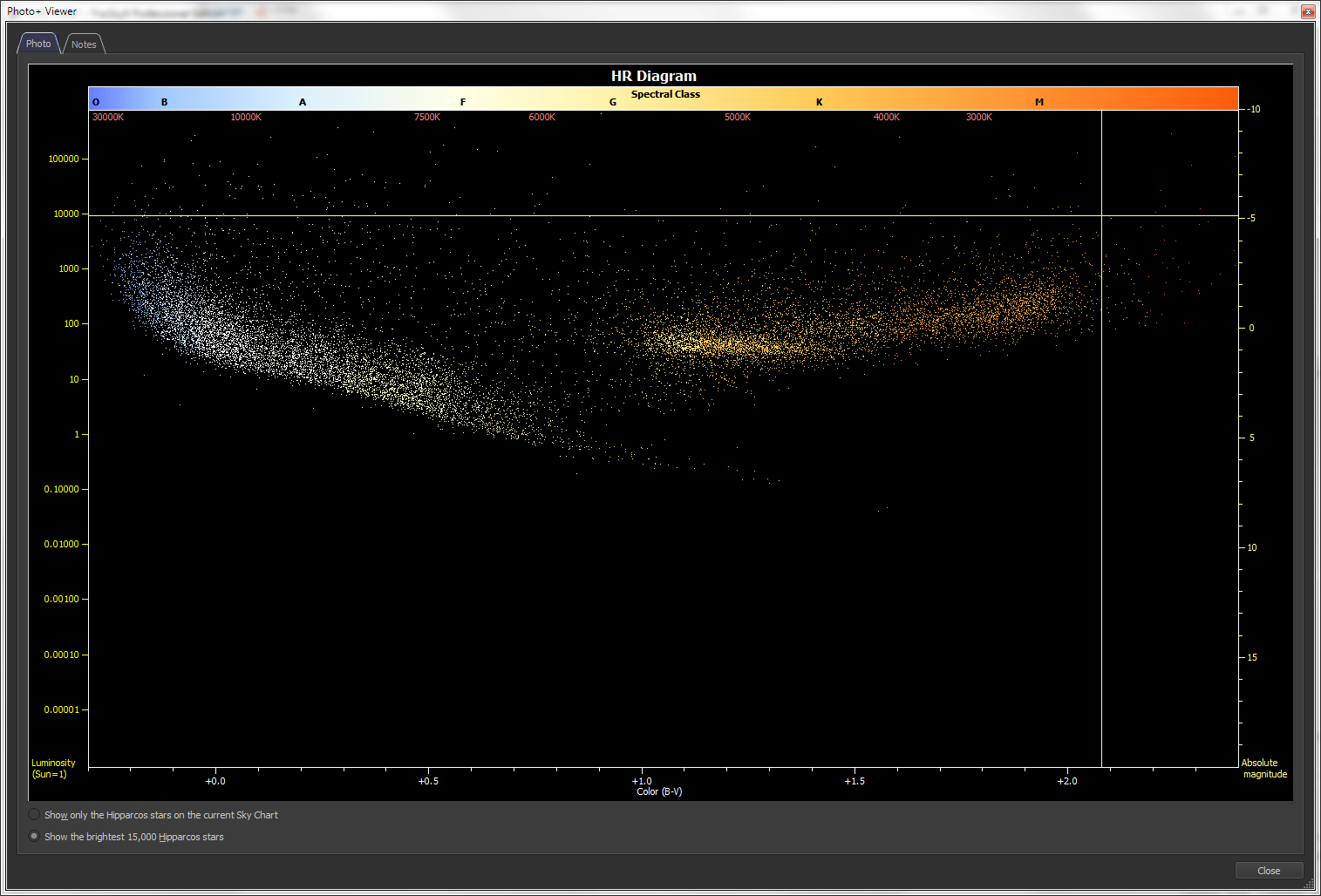
Hertzsprung-Russell
Wide-field
|
The simplified observing list includes a What's Up? query that lets you specify the viewing time, your optical aid (naked eye, binocular, or small telescope) and which objects you're interested in seeing tonight; TheSky's What Up? command generates a report for you, complete with fascinating descriptions about many deep-space objects, sample photographs of the object (when available), and Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagrams for stars. You can scroll through each object in the report and watch the Sky Chart update to show you exactly where to look for the object. |
|||||||||||||
|
Create and Show Field of View Indicators (FOVIs)
|
FOVI
|
Choose your equipment from a database of hundreds of telescopes, eyepieces and cameras or define your own, then show an overlay on the Sky Chart.
|
||||||||||||
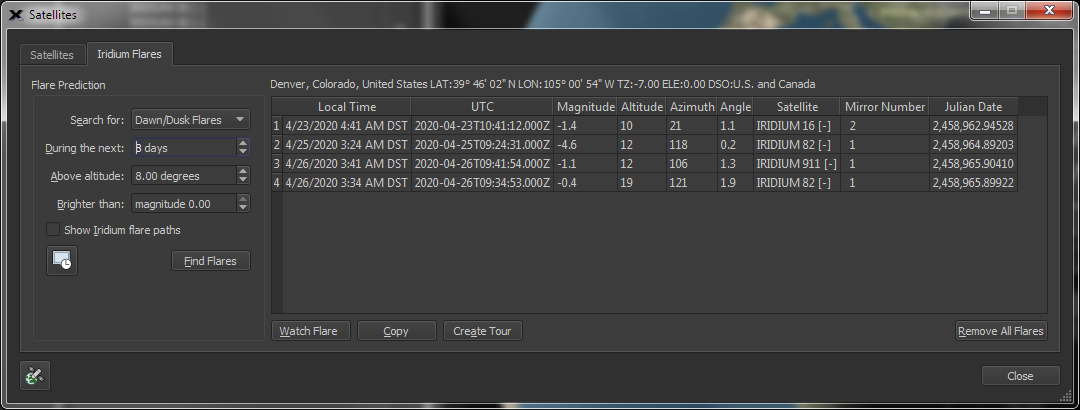
|
Iridium
|
Predict and watch simulated Iridium Flares directly from TheSky.
|
|||||||||||||
|
Tour
|
TheSky includes animated tours that you can watch, learn, or show others basic astronomy concepts. Supplied Tours include:
|
|||||||||||||
| Tabbed/Dockable/Floating Windows |
Tabbed windows on the Sky Chart.
|
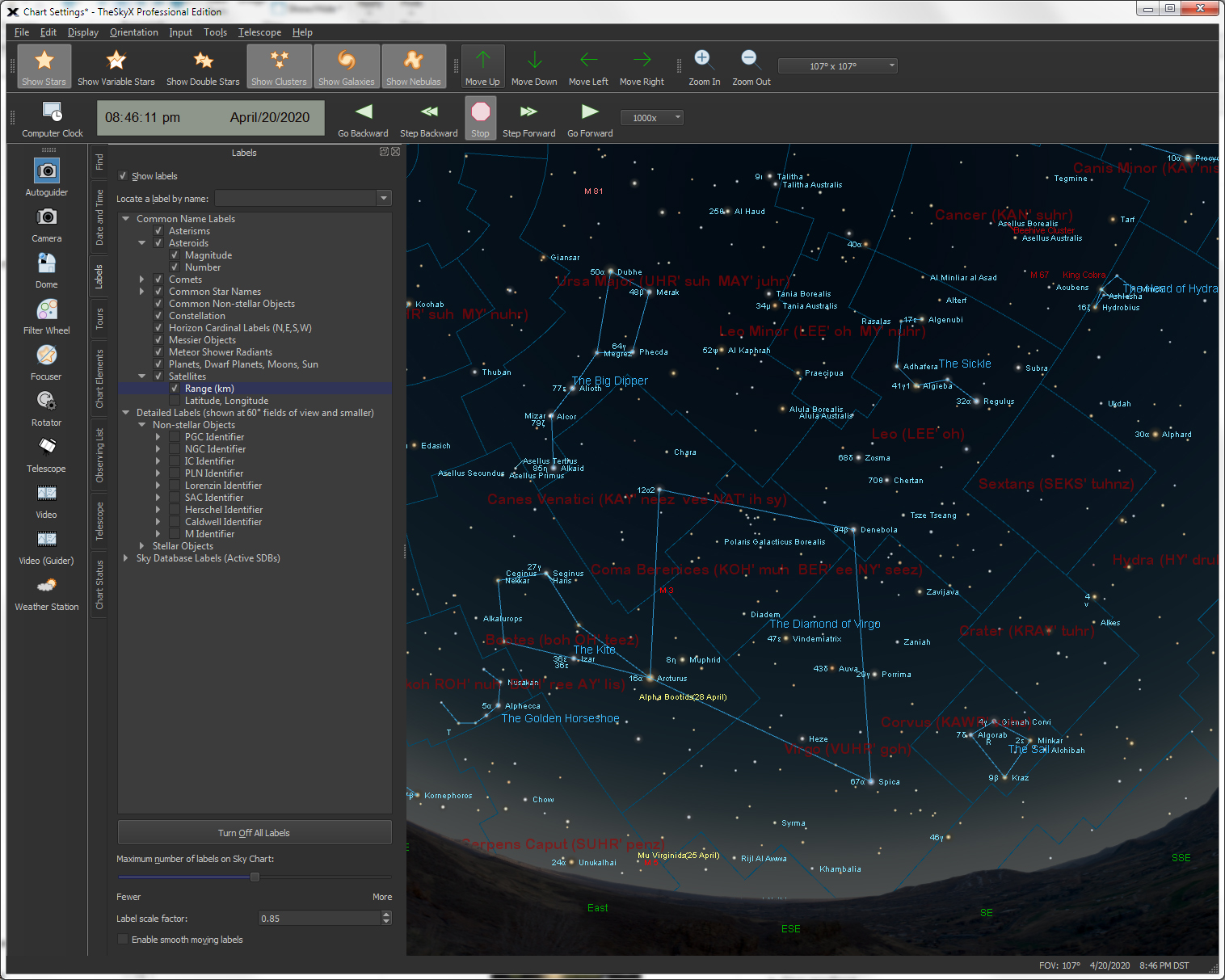
By default, commonly used features can be accessed by clicking the List of the standard docking windows: Tours window - Watch animations related to many interesting astronomical concepts. Find window - Easily locate any object by name, catalog number and many other designations. Chart Elements window - Lets you turn on and off, or filter by
Labels window - Turn on and off the names of objects, including:
Photos Each tab represents a separate window that can be moved and sized to your liking. |
||||||||||||
|
Simple
A list of common names that match the letters you type appears automatically. Advanced tab
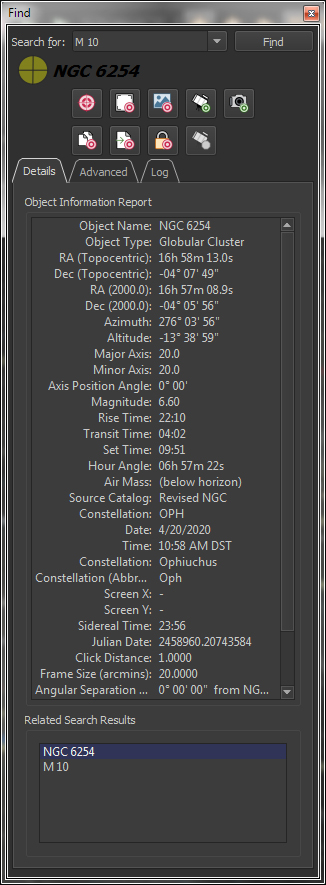
All object in TheSky's |
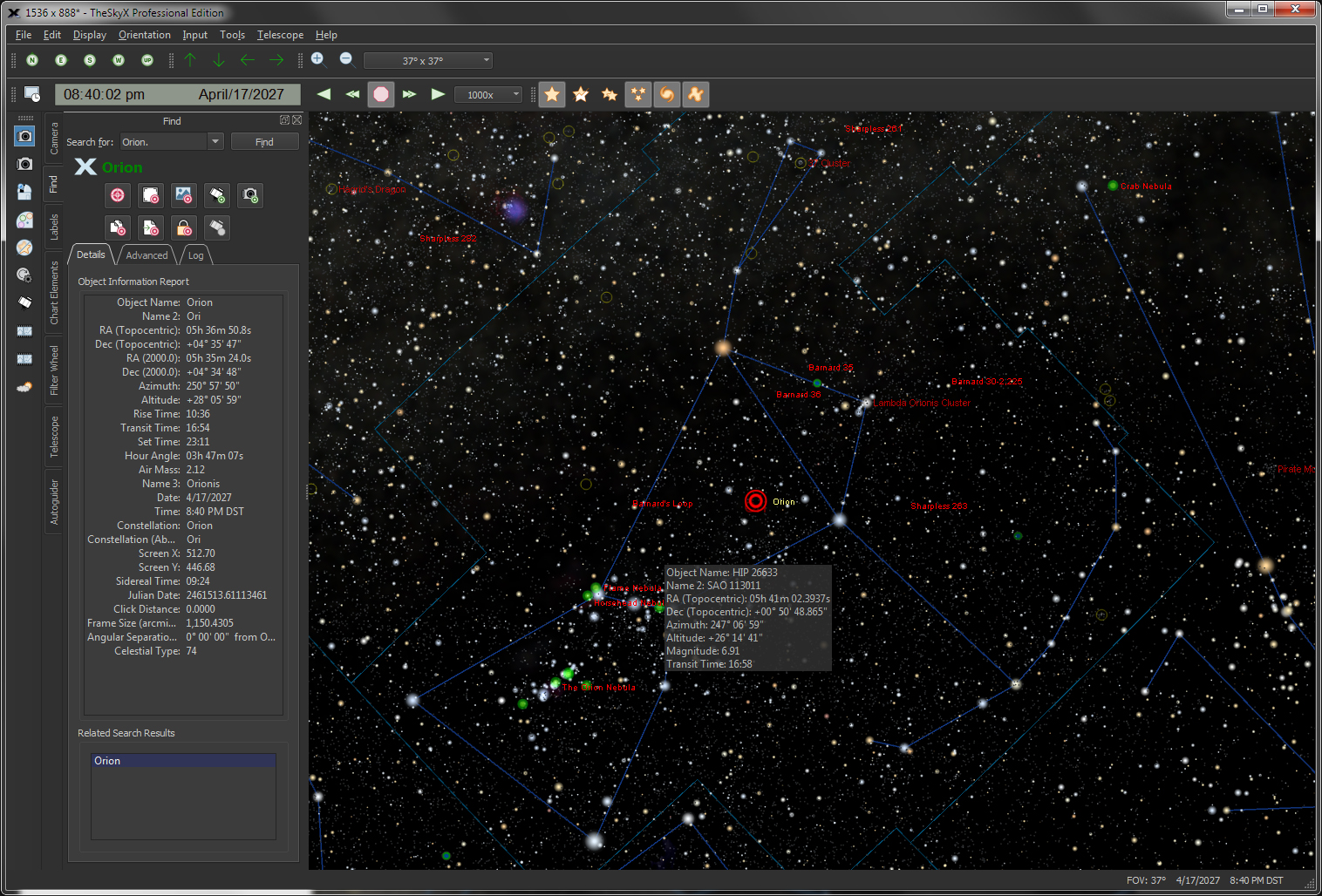
The friendly, powerful Find command lets you easily locate any object in TheSkyX's astronomical databases.All objects in the databases are listed in a "tree list" and sorted by type (star, double star, galaxy, cluster, etc.). Just double-click on the name to find it, or specific classification, including: Finding Stars by:
Finding Non-stellar objects by:
Finding Solar System Objects:
Finding the Constellations by:
Find 70 Common Asterisms The object's name appear in green letter if it's currently above the horizon, or in black italicized letters when it's below the horizon. |
|||||||||||||
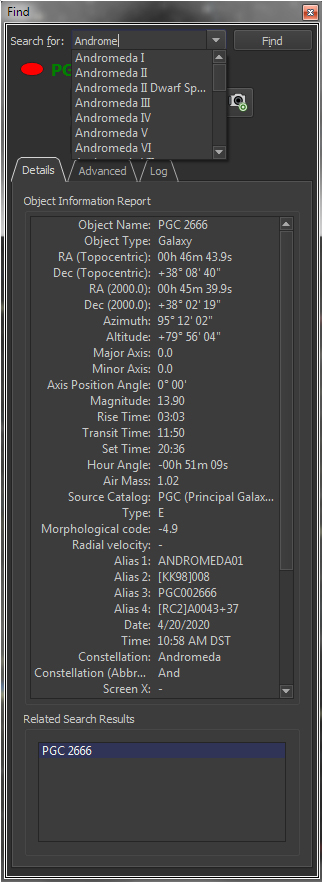
| Get Detailed Information on Celestial Objects |
Object |
Click on any object, or use the Find
*Please note that not every database or every Sample Object Information The table below lists the typical information displayed for
|
||||||||||||
| Select Different Photographs for the Panoramic Horizon |
Software New Mountain
|
Choose from several supplied custom panoramic horizons, including:
|
||||||||||||
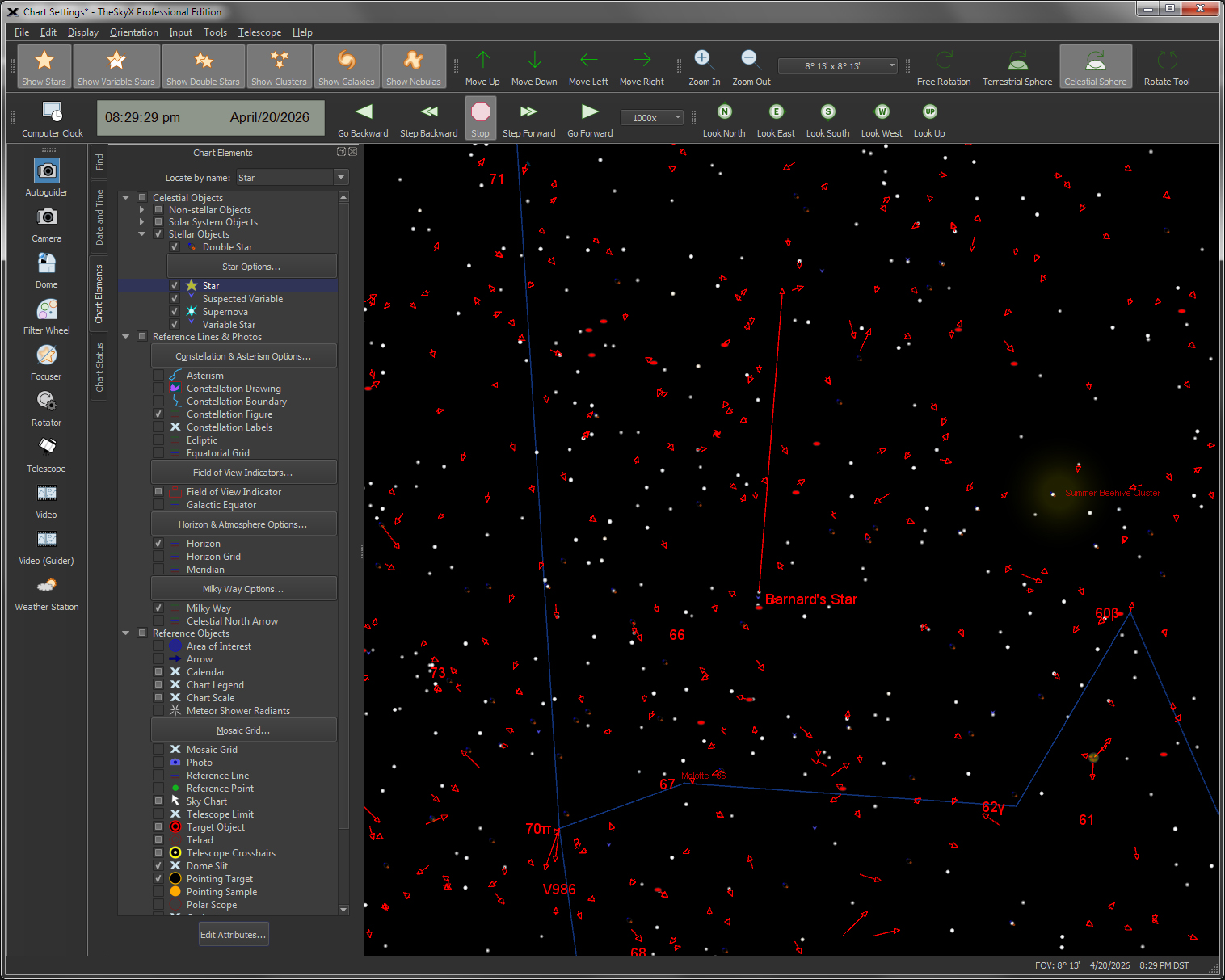
| Quickly Set Chart Options with Chart Elements |
Chart
|
Turning on and off individual, selected or all object classifications or "chart elements" is easy with the Chart Elements window. |
||||||||||||
| Show Reference Lines and Photos |
Reference Lines and Reference Photos
|
Show the following reference lines and reference photos. Constellation Figures from:
|
||||||||||||
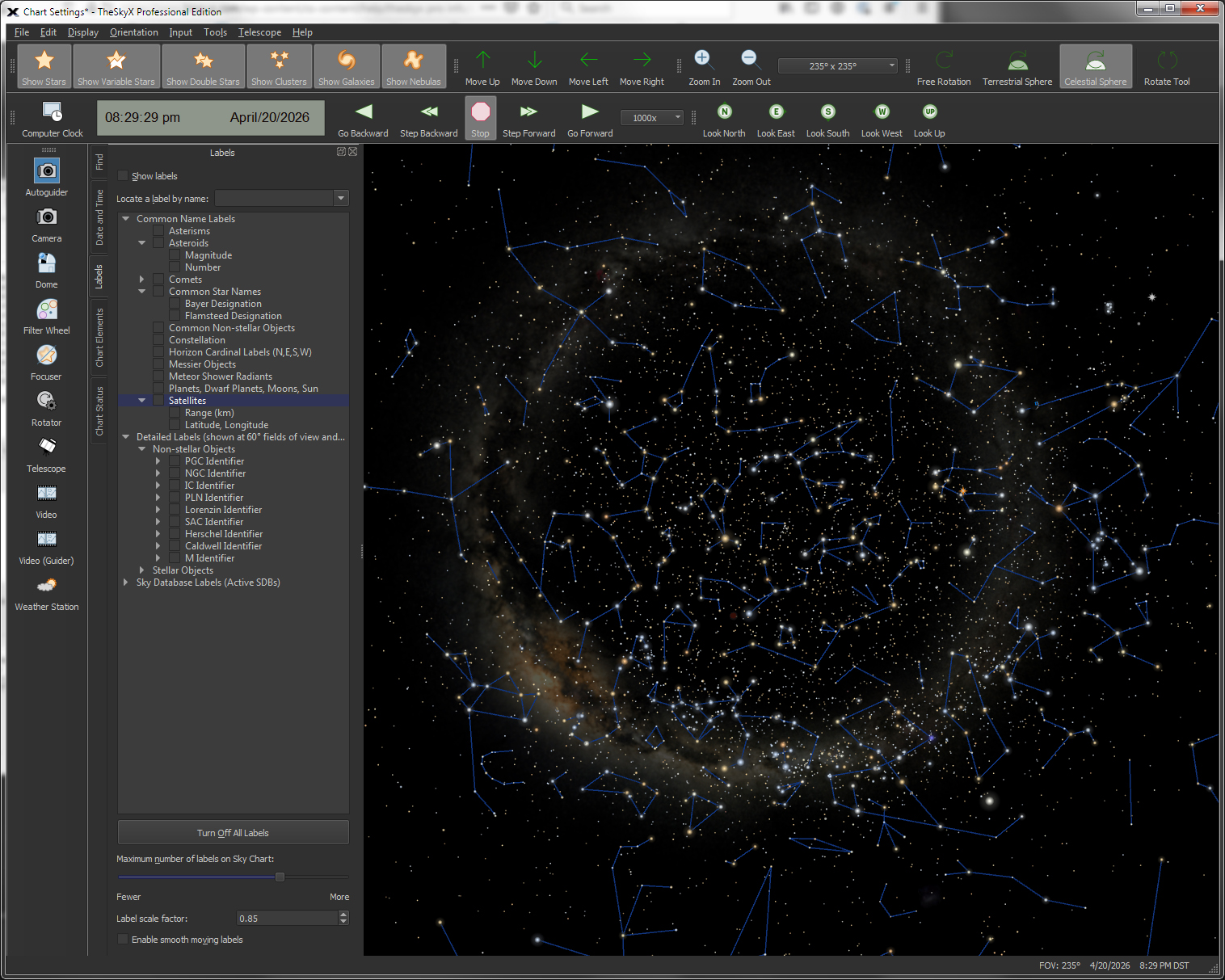
| Show Object Names (Object Labels) |
Object Name Labels
|
TheSky can show the names and labels for the following:
|
||||||||||||
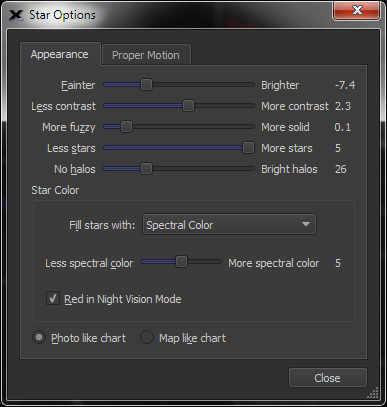
| Configure Appearance of Stars |
Sample
Star
|
Adjust the appearance of the stars by:
|
||||||||||||
| Customize Tool bars to Access Commands You Want |
Look
Orientation
Tool
|
Six standard tool bars contain buttons to access many frequently used commands. You can also add your own custom tool bars for the commands you The position of the tool bars can be customized. Show them as floating windows, or drag and drop them anywhere along the edges Star Chart window. |
||||||||||||
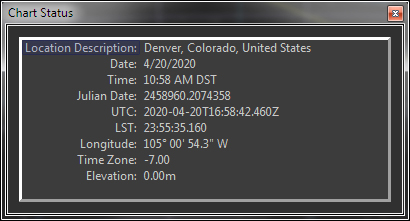
| Chart Status window |
Chart Status window with configurable report |
The Chart Status window shows a continuously updated information about the current chart. Choose from the following list of status report options:
|
||||||||||||
| Show/Hide Scroll Bars |
Chart with optional scroll bars turned on
|
Show/hide horizontal and vertical scroll bars for easy chart navigation. |
||||||||||||
| Look North, South, East, West or Up |
|
Never get lost in space! Automatically adjust the star chart for your location to look North, South, East, West or straight up (at the Zenith).
|
||||||||||||
| Zoom Box |
Zoom Box
|
Click and drag the "zoom box" on the chart to magnify (or |
||||||||||||
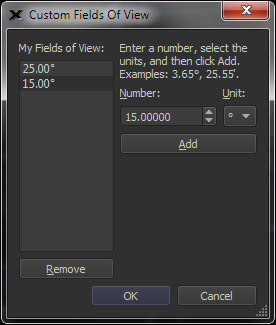
| Zoom to Pre-defined Fields of View |
Custom Field of View window.
|
Built-in command to show the following fields of view:
Or, define any number of custom fields of view using the Custom Fields of View dialog. |
||||||||||||
| Navigate the Celestial Sphere |
Navigate
Navigate
|
The Navigate window let's you:
|
||||||||||||
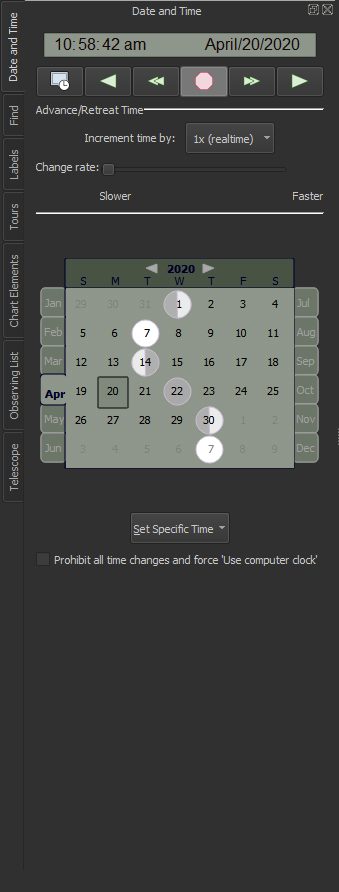
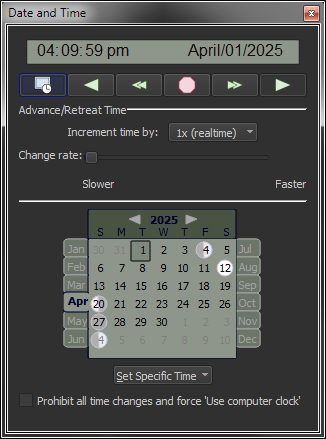
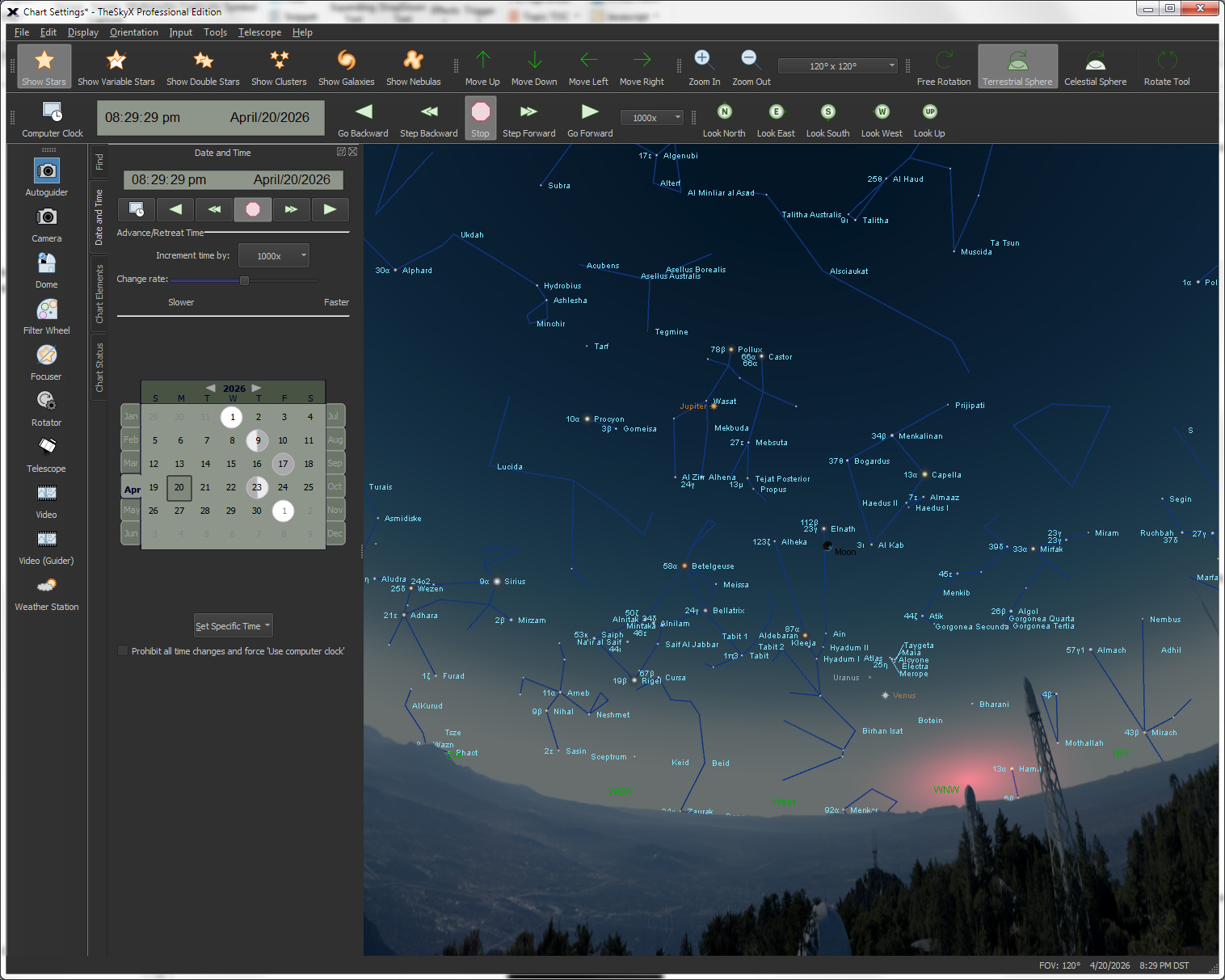
| Control the Date and Time |
The
Custom
Date |
Input any date from 4,712 B.C. to A.D. 10,000 and any time to show a beautiful star chart for your location. The Date & Time tab on the Command
The Date & Time tab allows you to specify specific times, including:
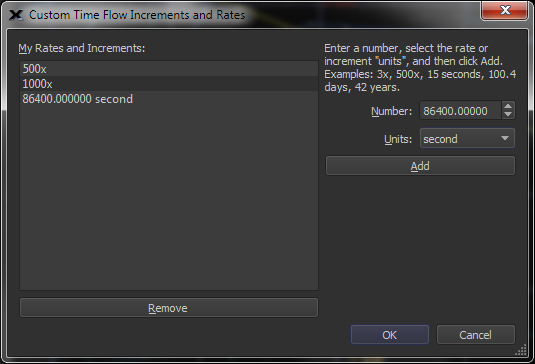
The Date & Time tab allows you to control the rate that time changes, or the increment of time to advance or retreat in time. The default increments include:
You can define custom increments and rates using the Custom Time Flow Increments and Rates dialog. The Date & Time toolbar allows you to set the Date & Time as well as specify the direction
|
||||||||||||
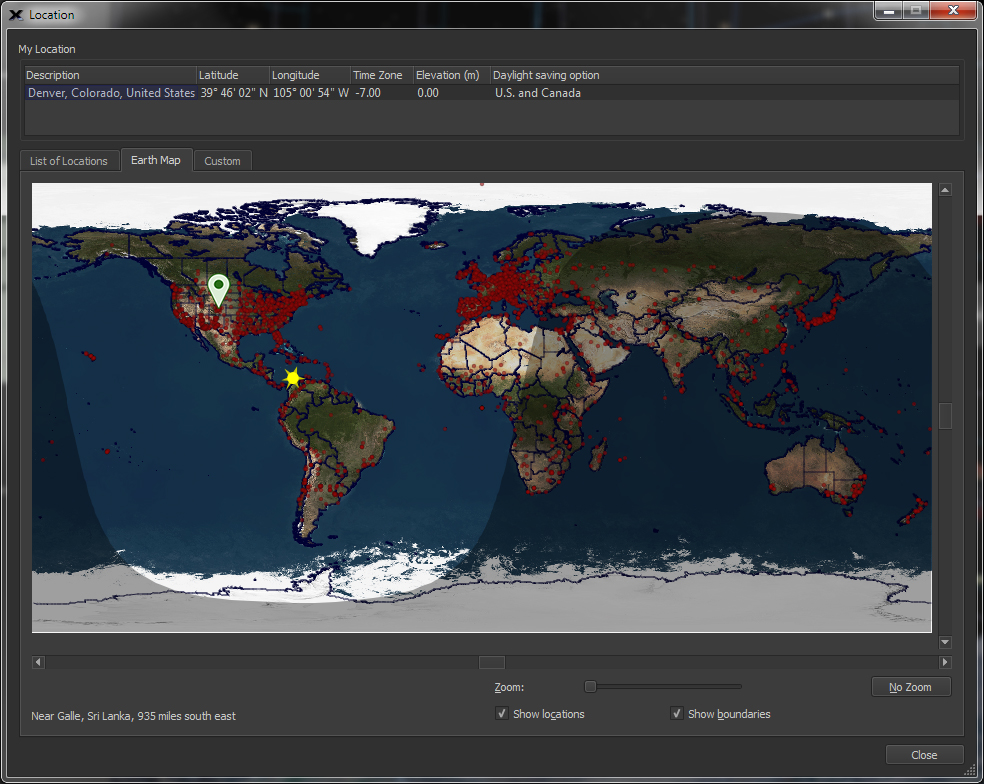
| Choose your location on Earth |
Earth
|
By default, your location on earth is detected automatically from the web. Or,
|
||||||||||||
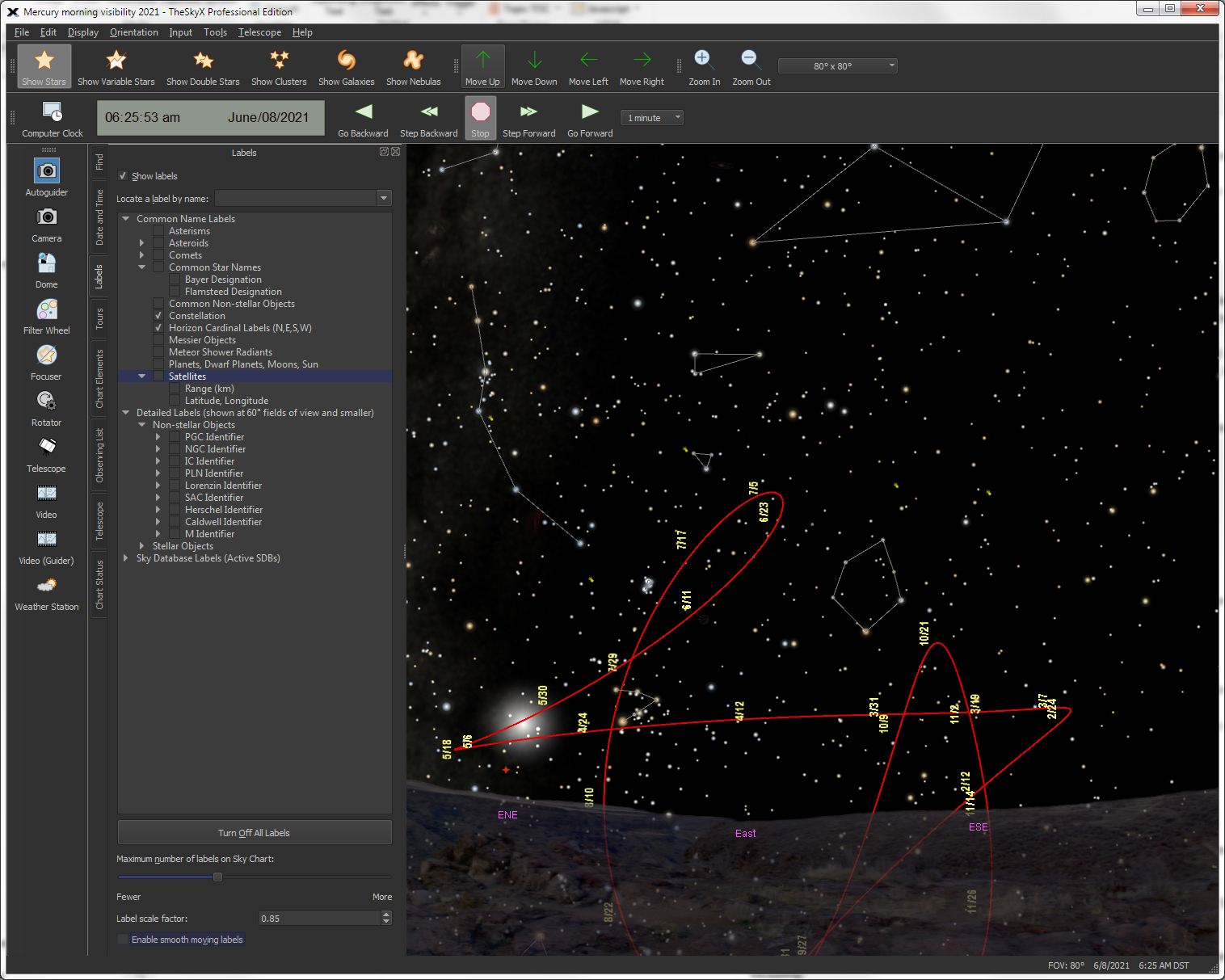
| Create Solar System Object Paths |
Mercury
|
Create a "path" that represents the future or past positions |
||||||||||||
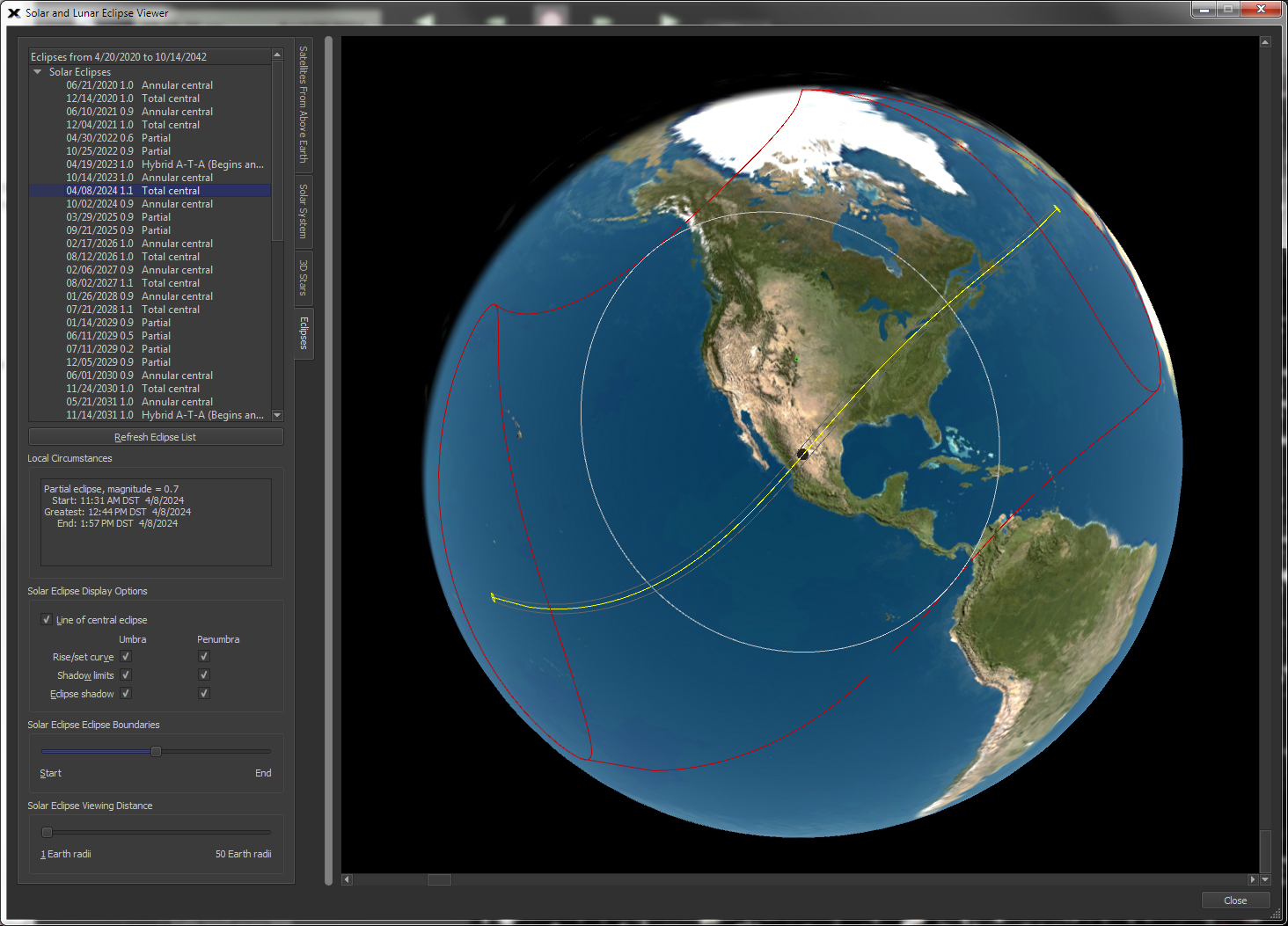
| Find and View Solar and Lunar Eclipses with the Eclipse Viewer |
Solar
Example
|
When is the next solar eclipse? Where it visible on Earth? You'll be able to answer these questions, learn about the dynamics of solar and lunar eclipses and more using the Solar and Lunar Eclipse Viewer. Solar Eclipses TheSky shows every solar eclipse for the next twenty years (or so) from the current date (starting from any date). Select an eclipse from the list and the three-dimensional view of the Earth gives the local circumstances:
You can adjust the viewing distance from Earth using the Solar Viewing Distance Slider. Lunar Eclipses As with solar eclipses, the next twenty years of lunar eclipses are listed. Select one from the list to view it's local circumstances, including:
When a lunar eclipse is selected,
|
||||||||||||
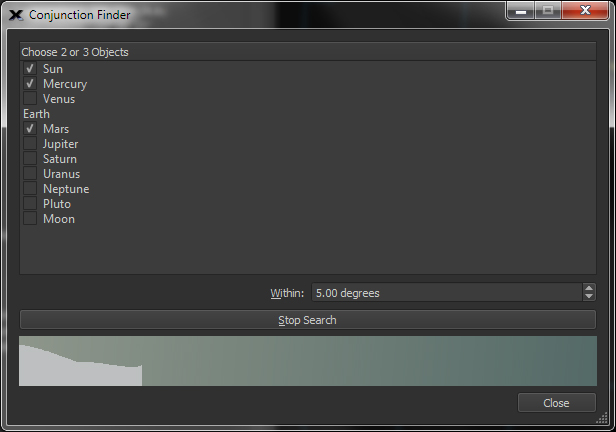
| Find Conjunctions with the Conjunction Finder |
Conjunction
View
|
Select any 2 or 3 planets (or the Sun and Moon) to find the future conjunctions of these bodies. For each conjunction that is located, |
||||||||||||
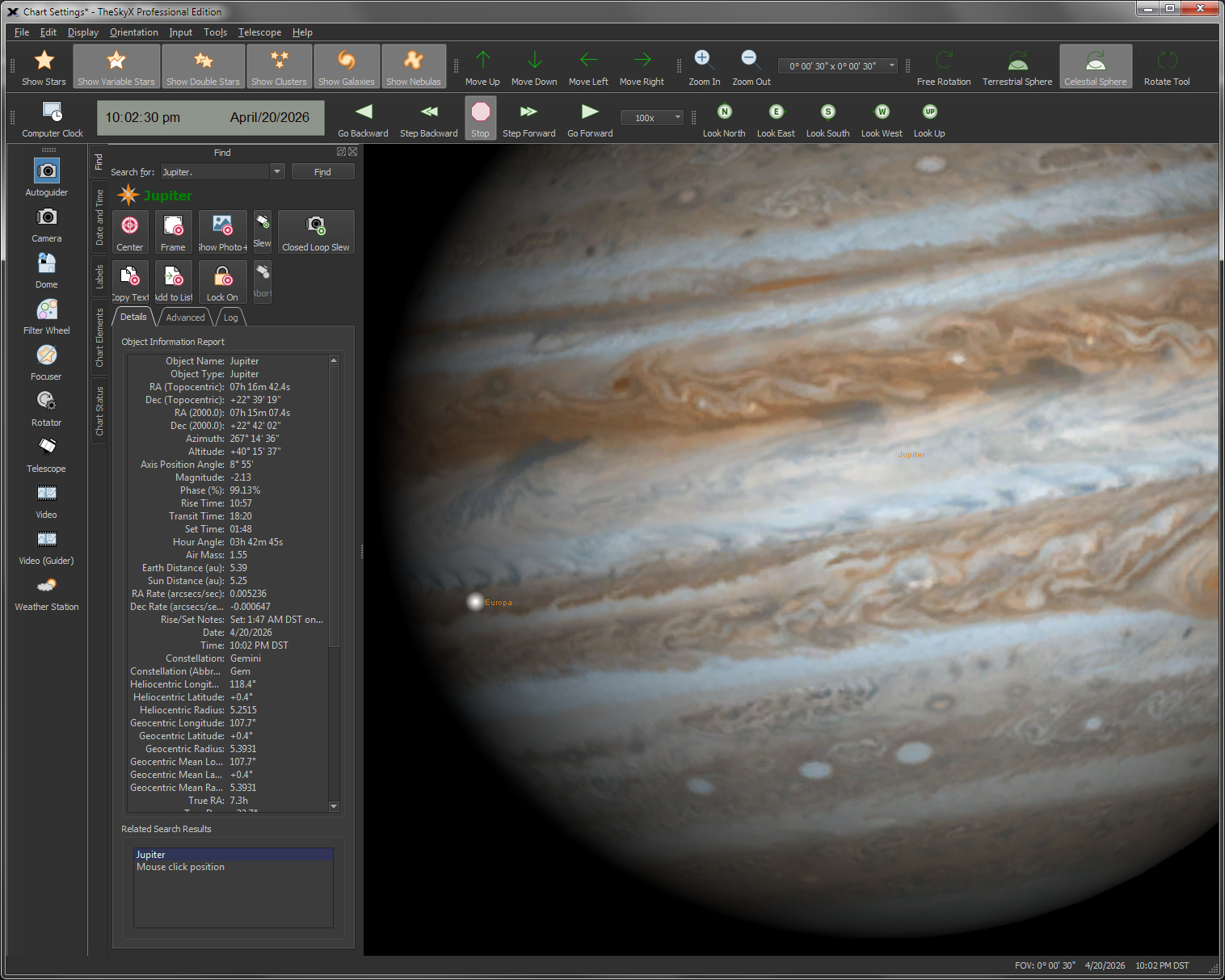
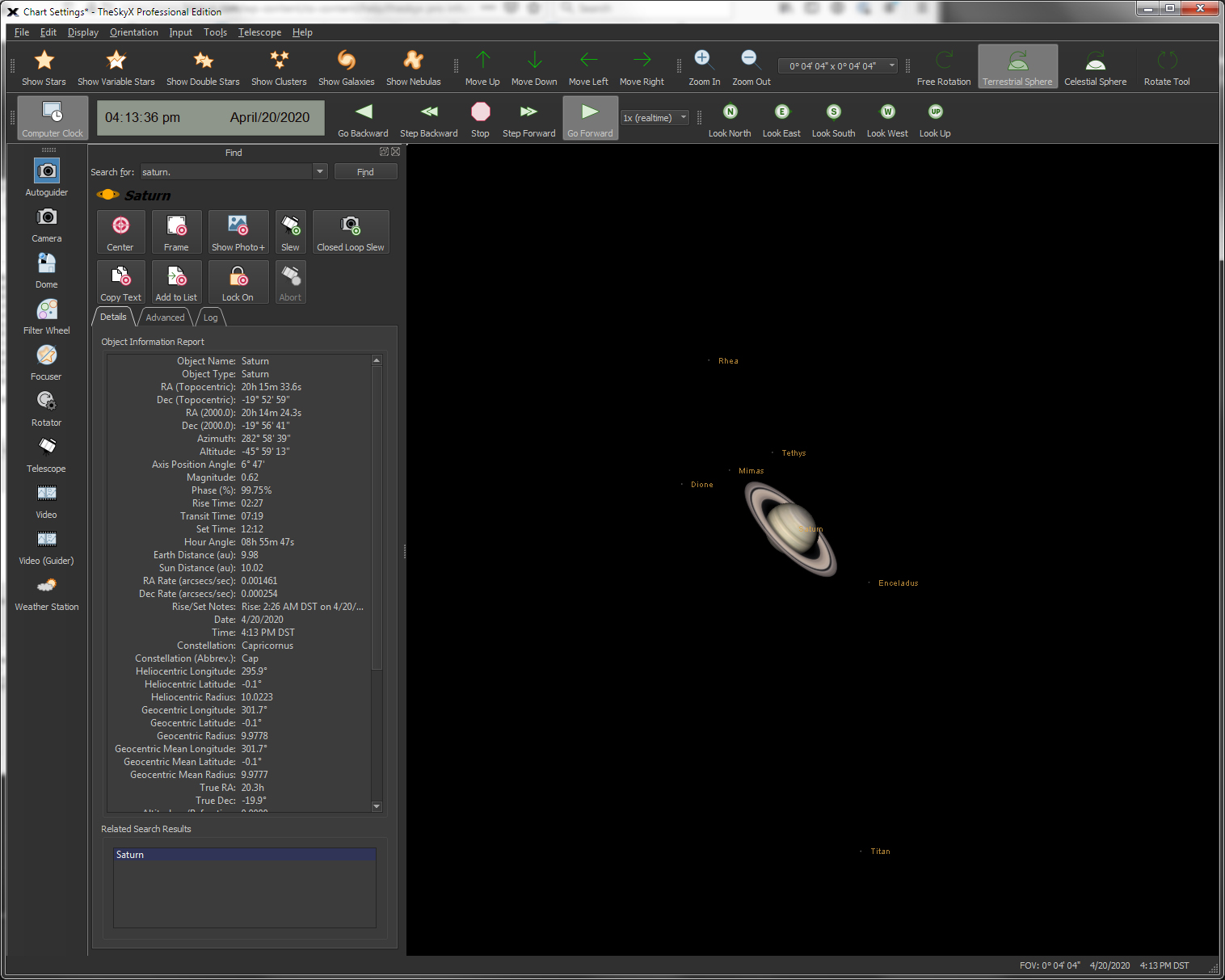
| Show the Positions of the Major Moons of Jupiter and Saturn |
View
View
|
View the positions of Jupiter's and Saturn's major moons. |
||||||||||||
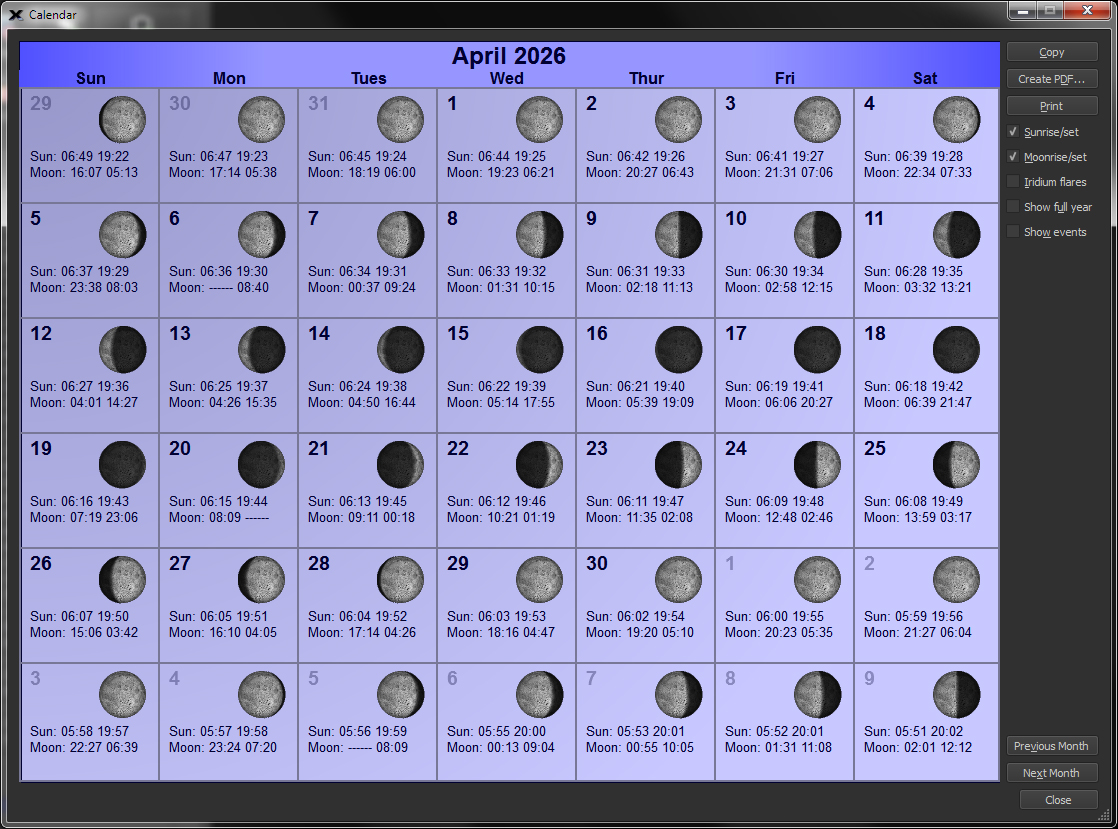
| Display or Print Calendars showing the Moon's Phase and other information |
Monthly
|
Show a calendar of any month with the phases of the moon, as well as sunrise, sunset, moonrise, moonset, and Iridium Flare occurrences. A full year's calendar can be shown, too. The calendar can be saved (or exported) as a PDF file.
|
||||||||||||
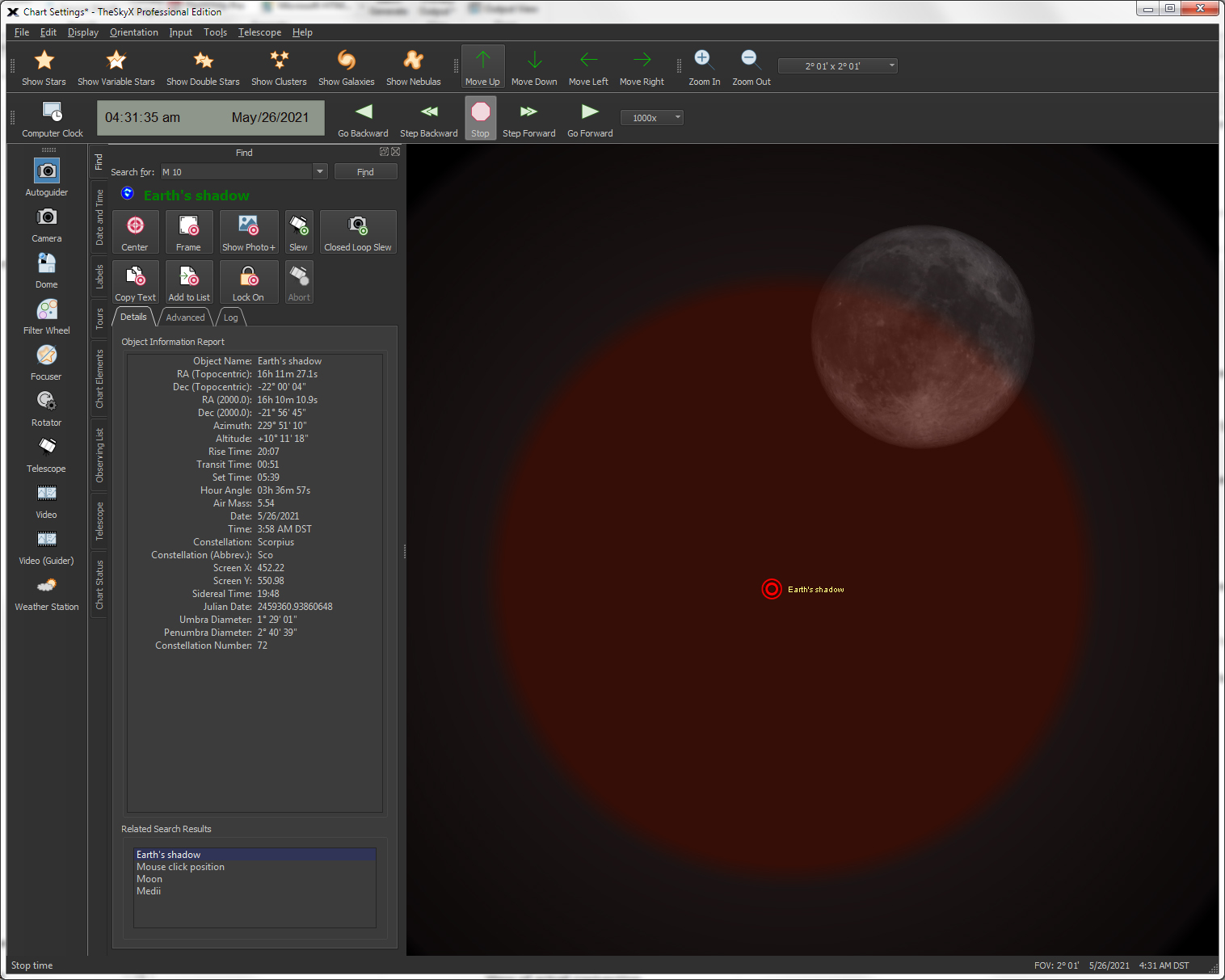
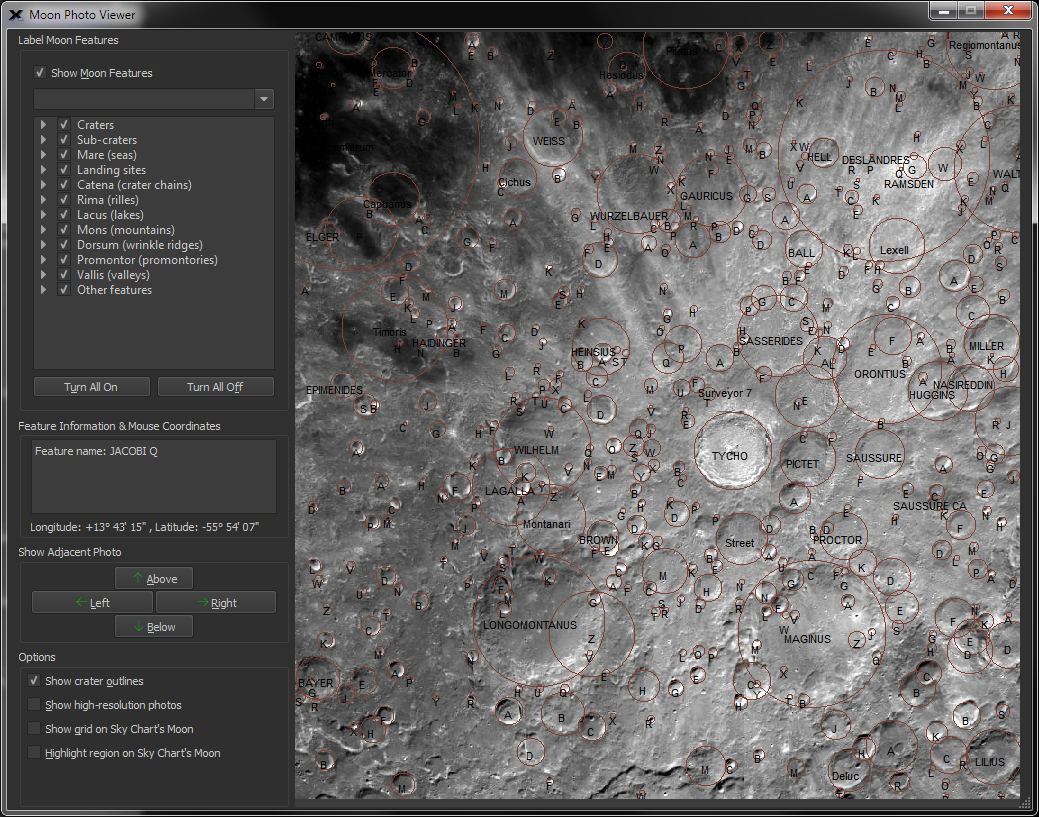
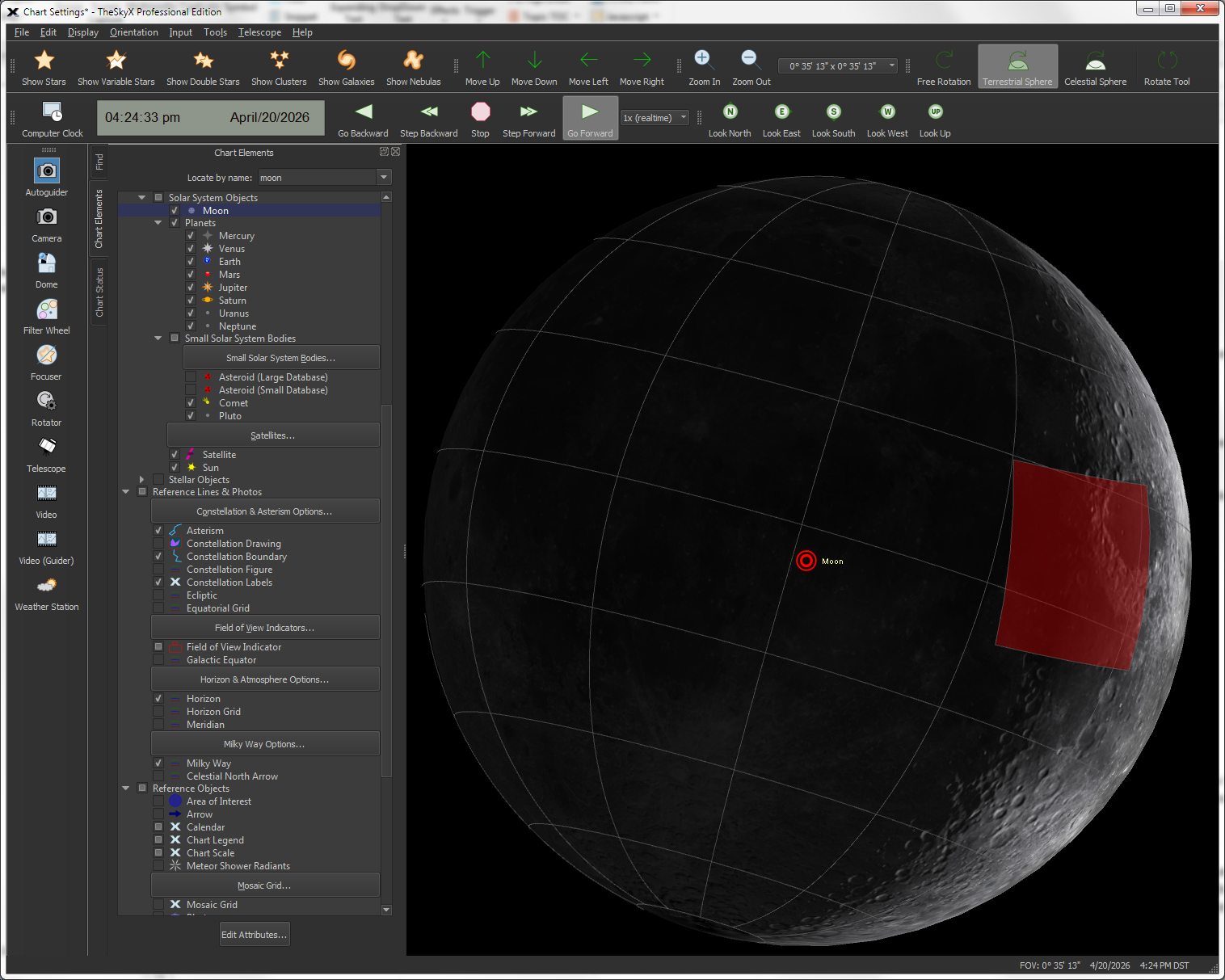
| View High-Resolution Images of the Moon using the Moon Viewer |
Moon
Location |
The interactive Moon Photo Viewer is a powerful tool that can:
Identify and get feature specific
When the "Highlight Photo's Location |
||||||||||||
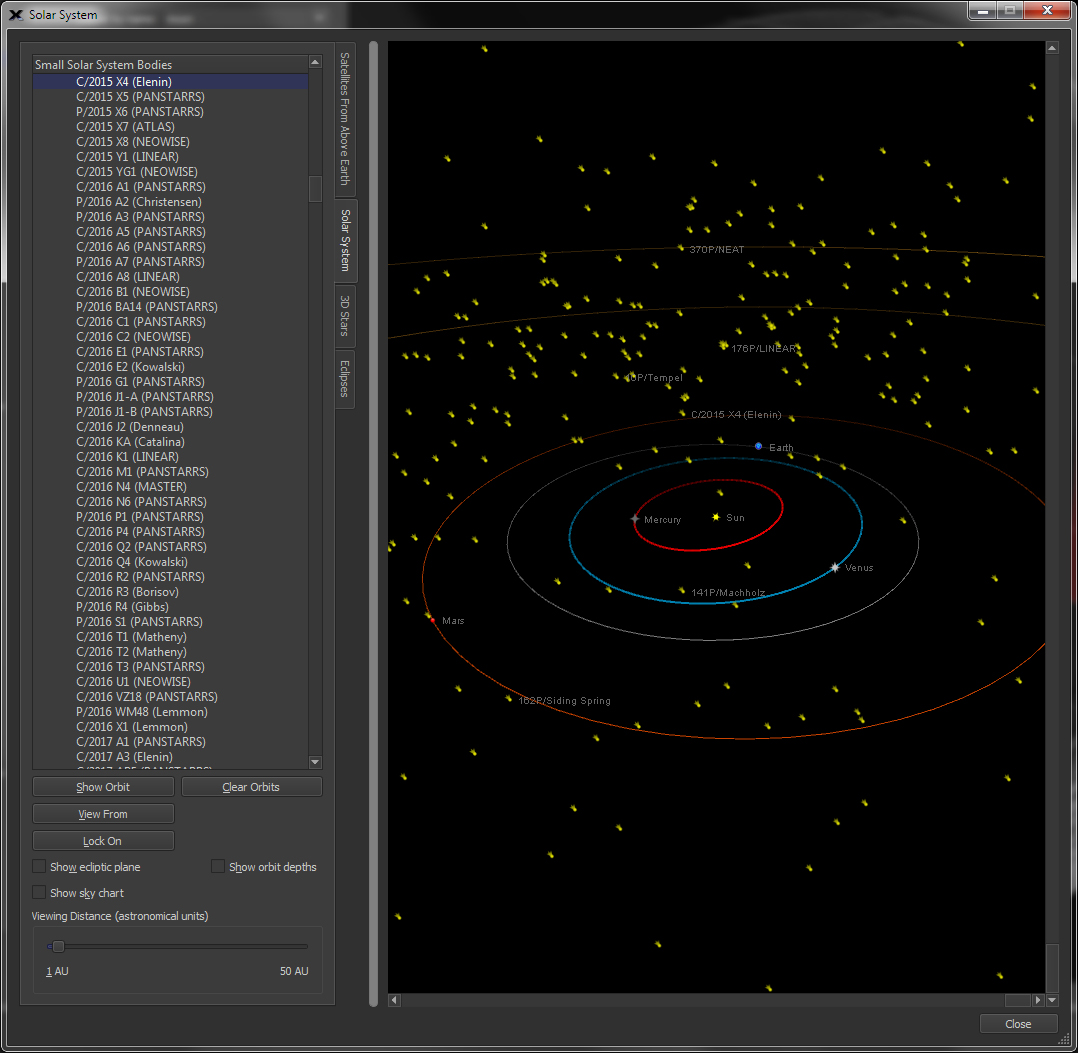
| View the Solar System in Three Dimensions using the 3D Solar System Viewer |
Three
|
Use this command to toggle between looking at the sky from Earth or from outer space (anywhere inside our solar system). When this command is enabled, the starry background is turned off by default and only the objects in our solar system The default location is an arbitrary point in space. |
||||||||||||
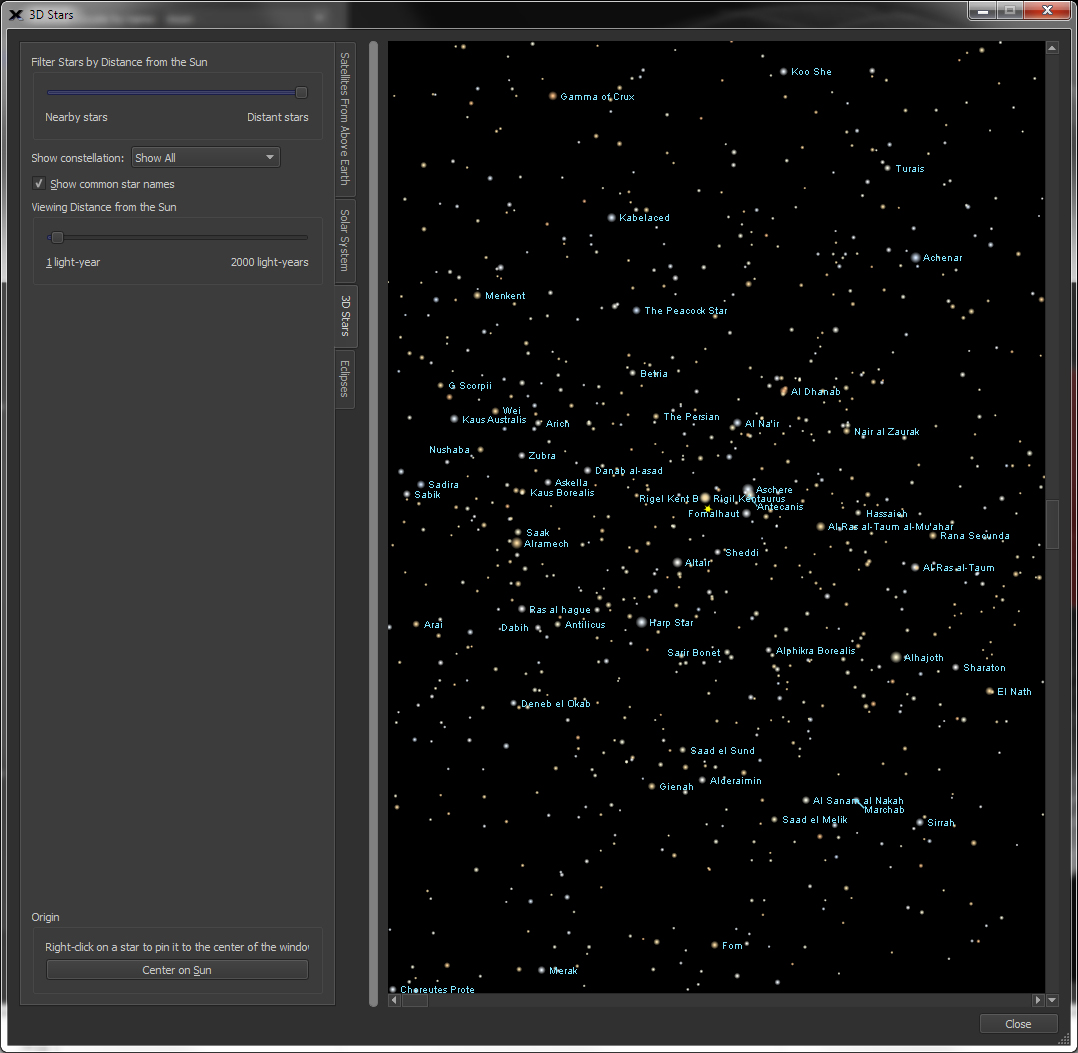
|
3D view of the
|
View the stars in three dimensions with the 3D Stars tool. You can zoom, pan and scroll around the universe to learn about the relative Even isolate any of the 88 constellations and view only the stars within its boundaries. |
|||||||||||||
| Show Detailed Constellations Figures |
Bevis Constellation
|
Show detailed drawings for all or selected constellations. |
||||||||||||
| Simulate the Daytime Sky |
Sunset
|
The Daytime Sky Mode lets you simulate and how the sky looks during daytime, as well as dawn and dusk. |
||||||||||||
| View in Full Screen Mode |
Full
|
Have the Sky Chart occupy the entire desktop in Full Screen mode. |
||||||||||||
|
|
Show the entire screen (and the entire desktop) predominantly red to preserve the eyes' dark adaptation (or night vision).
|
|||||||||||||
| Show the Chart as a Mirror Image |
Show
|
Mirror image reverses the Sky Chart, left-to-right. This lets you view |
||||||||||||
| Show Photo-Like or Map-Like Star Charts |
|
Chart mode displays Sky Chart to look more like what you would see in a book of star charts, or how a printed chart might look. |
||||||||||||
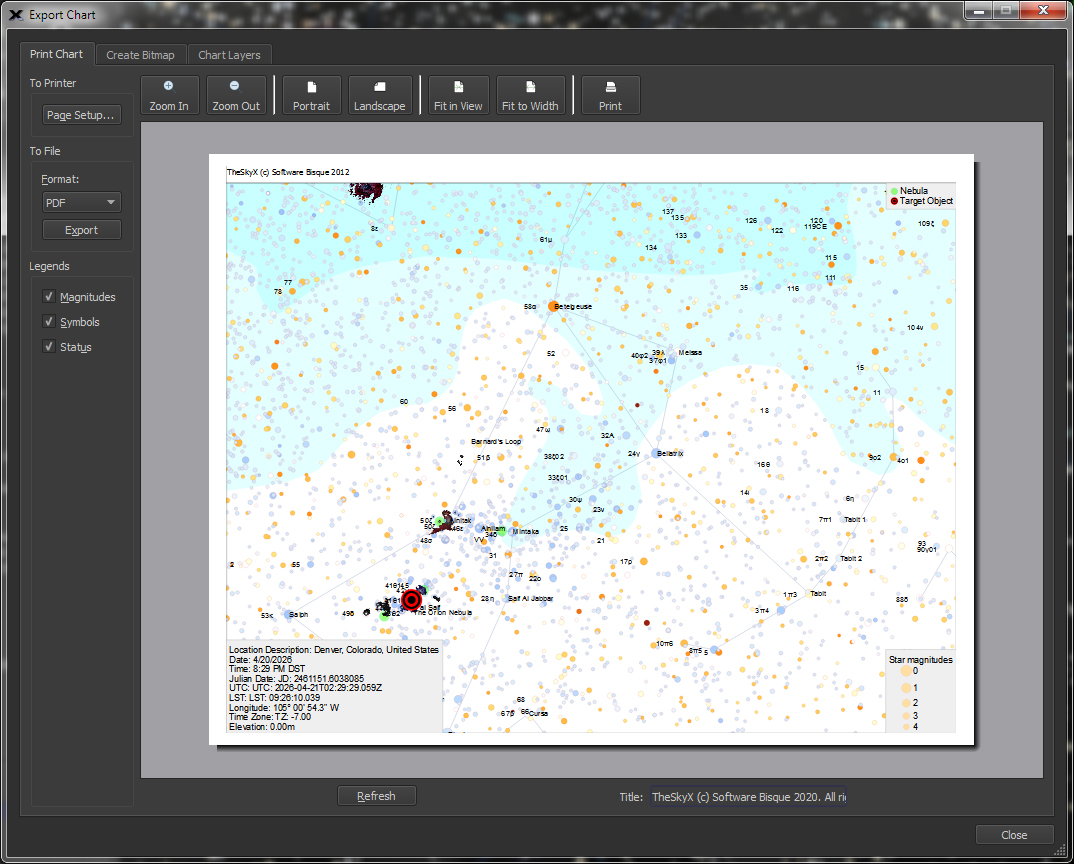
| Create Publication-Quality Star Charts. Graphics and PDF Output |
Exported
|
Sky Charts can be exported in portable network graphs (PNG) format, or saved in portable document format (PDF) for publication of charts and graphics to your astronomy club newsletter or web site.* *Please include the text "Copyright Software |
||||||||||||
| Print and Export Star Charts |
|
Print high-resolution star charts on your printer for field use. |
||||||||||||
| Click to Drag the Sky Chart to Change Field of View |
|
Click and drag the mouse and drag the sky chart to change its position.
|
||||||||||||
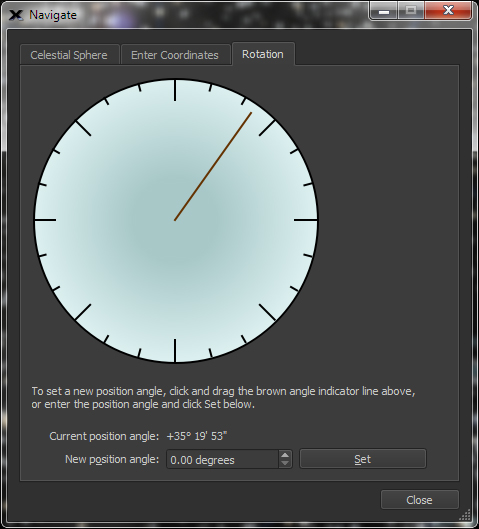
| Rotate the Sky Chart to any position angle |
Screen
|
Use the Rotate tab on the Orientation > Navigate window to rotate the Sky Chart to any angle to match your field of view or photo's |
||||||||||||
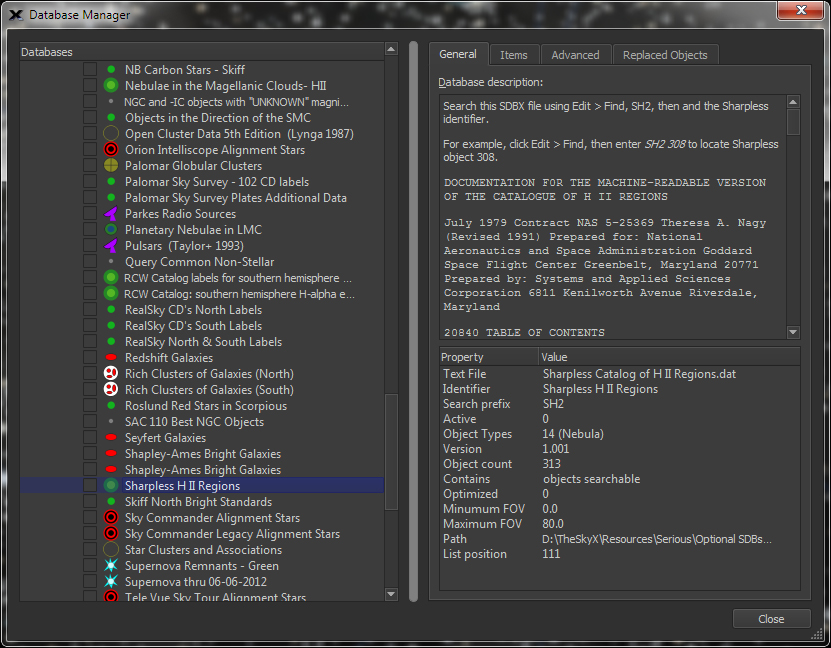
| Database Manager to Add/Remove Core and Additional Sky Databases (SDBs) |
Database
|
Use the Database Manager to:
|
||||||||||||
| Compute and View Stellar Proper Motion |
Chart
Configure
|
Stars' proper motion lets you:
|
||||||||||||
| Friendly and Extensive User Guide |
|
TheSky User Guide teaches you many fundamental principles about astronomy and relates them to TheSkyX software. This document is available in three different digital formats to satisfy any preference:
Note that a printed copy of the 800+ page TheSky User Guide is not available. If a printed copy is required, Software Bisque can grant permission to have a copy printed and bound by your local printing shop.
|
||||||||||||
|
Wide
Zoomed
|
Simulate the celestial sphere, at any magnification from 235 degrees to 30 arcseconds. |
|||||||||||||
|
Limit |
Filter
and
|
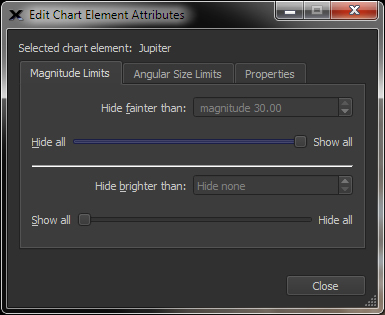
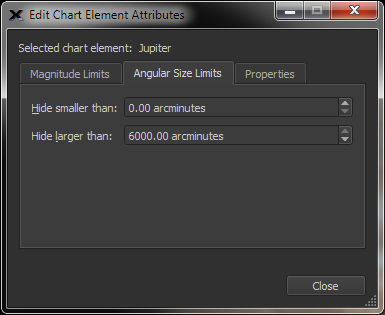
Select any object type (or all object types) and easily adjust the upper and lower magnitudes and the maximum and minimum angular sizes of objects that are shown on the Sky Chart. |
||||||||||||
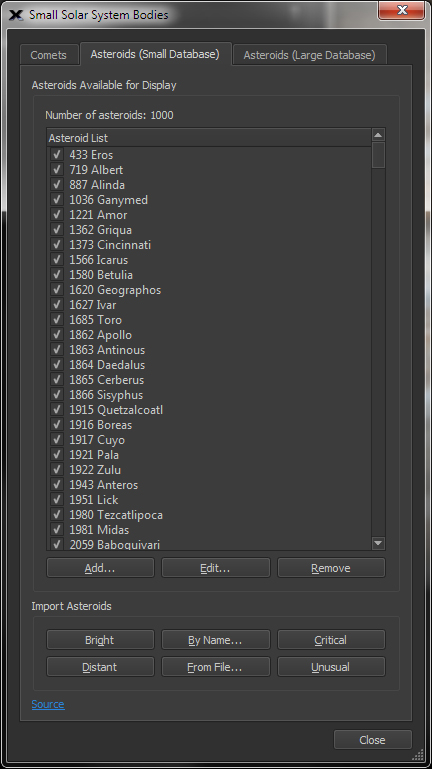
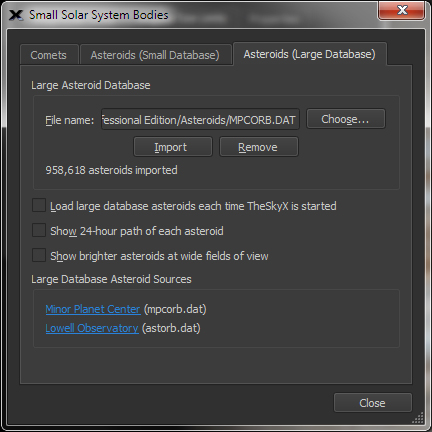
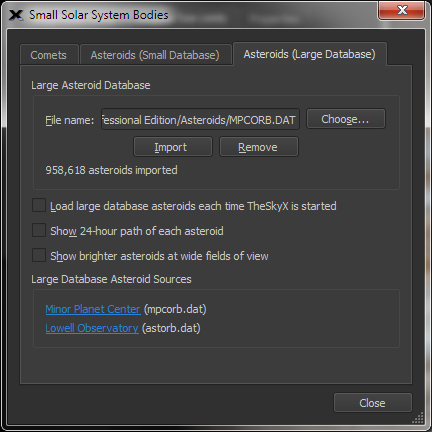
| Display Small Solar System Objects, including Comets, Asteroids and Man-Made Satellites |
Import
Import
Import
Import
|
|
||||||||||||
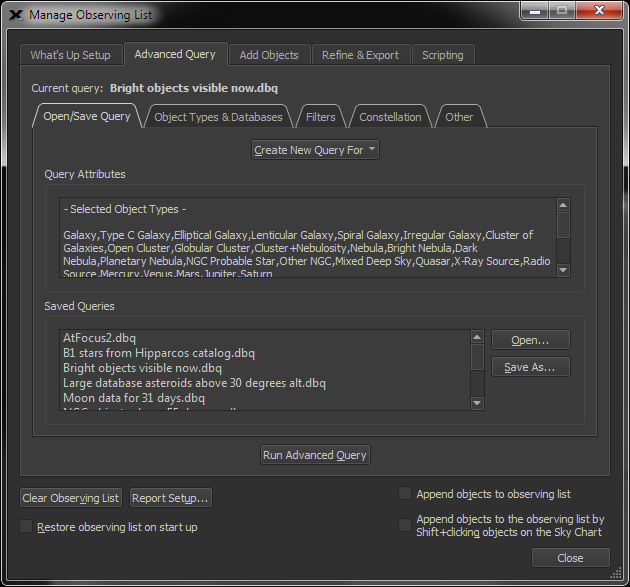
| Create Observing Lists |
Observing
Observing
Observing
|
TheSky makes generating an observing list from this complex query simple!The Create Observing List command in the Tools menu can be used to perform advanced searches or database queries that can be used to generate observing lists. The Advanced Query tab offers much more detail regarding your query of celestial objects than the simplified options on the What’s Up Setup tab.Suppose you want to create an observing list that contains all the double stars from the Washington Catalog of Double Stars that have a spectral type of G5 in Orion. |
||||||||||||
|
|
Astronomical Databases and Photos
TheSky Professional provides an extensive set of astronomical catalogs and the tools to quickly access information from them. The "core" databases include many industry-standard astronomical catalogs. They should meet your needs whether you're star hopping with your telescope, taking CCD images of faint galaxies, or computing sub-arcsecond astrometric positions of minor planets.
TheSky Pro also includes an extensive set of optional "non-typical" Sky Databases (SDBs) that contain many unusual or hard to find objects that may not appear on standard astronomical catalogs.
|
Database Category |
| Core Astronomical Catalogs |
| Solar System Objects |
| Catalog Cross References |
| Sky Databases (SDBs) |
| My Chart Elements |
| Optional Database Add On |
| Photographs |
TheSky Professional includes databases of celestial objects from the standard astronomical catalogs in the table below. Use TheSky Professional's Find Command to locate any object from any of these catalogs by name, catalog number or other standard cross references (where applicable).
| Catalog Type | Name of Catalog | Object Count and Limiting Magnitude | ||||||||
|
|
Hipparcos/Tycho Stellar Catalog |
TheSky's core star catalog for brighter stars contains 1.2 million stars (complete to about magnitude 12).
|
||||||||
| Gaia Star Catalog |
The complete Gaia DR2 catalog occupies over 1.2 TB of disc space and can be downloaded from the Gaia archive page. When configured to use the complete Gaia catalog, TheSky Professional’s Sky Chart displays every star from the Gaia If you do not have a super-fast internet connection, or do not want to clutter your computer’s drive with unnecessary data you may not need, TheSky Professional supports two Gaia star catalog subsets that should suit the needs of most: Small Gaia Subset: The smaller Gaia subset contains the RA, Dec, G/BP/RP mean magnitudes, spectral class, star distance in light years, stellar temperature, and proper motion for about 100 million stars that are equally distributed across the celestial sphere. It is ideal for determining the astrometric solutions. This database is included with TheSky's full installers. Large Gaia Subset: The larger Gaia subset contains 1.7 billion stars, with the same information as the smaller subset described above. Successful Image Links are possible using optical systems that produce fields of view as small as about 3 arc minutes. This database is available on the Database Add On Version 3. Gaia Catalog Subsets
|
|||||||||
| Legacy star catalog support
Hubble Guide Star Catalog (GSC) Version 1.2, NOMAD, and the UCAC (versions 2, 3 and 4) |
The Gaia DR2 star catalog supersedes these legacy star catalogs | |||||||||
| Washington Catalog of Double Stars (WDS) |
99,068 double stars
|
|||||||||
| Struve Double Star Catalog |
4,307 |
|||||||||
| General Catalog of Variable Stars (GCVS) |
37,383 |
|||||||||
| New Suspected Variable Star Catalog (NSV) |
14,812 |
|||||||||
| New General Catalog (NGC) from the NGC/IC ProjectNGC/IC Database Copyright Notice |
7,840 |
|||||||||
| Index Catalog (IC) from the NGC/IC ProjectNGC/IC Database Copyright Notice |
5,382
|
|||||||||
| Tomm Lorenzin 2000+ Catalog |
2,088
|
|||||||||
| Herschel Catalog |
400
|
|||||||||
| Caldwell Catalog |
109 |
|||||||||
| Messier Catalog |
110 |
|||||||||
| Saguaro Astronomy Club (SAC) Database |
10,580
|
|||||||||
| Catalog of Principle Galaxies (PGC 2011) |
1,670,818 |
|||||||||
| Arp Peculiar Galaxies |
338 |
|||||||||
| PK Planetary Nebula Catalog (PLN) |
1,455
|
|||||||||
| Abell Clusters of Galaxies |
2,712
|
|||||||||
| Galactic Globulars |
2,495
|
|||||||||
|
Sun Mercury Venus Earth Earth's Mars Jupiter Io Ganymede Europa Callisto Saturn Enceladus Mimas Tethys Dione Rhea Titan Hyperion Iapetus Uranus Neptune |
22 |
|||||||||
|
Asteroids (minor planets) |
TheSky can show all known asteroids. At this time, there are about
|
|||||||||
|
|
Comets |
1100 comets can be imported and displayed at a time. The orbital elements can be updates from the web directly within TheSky. |
||||||||
|
|
Pluto |
Demoted from a planet to a small solar system body, but still one of our favorites! |
||||||||
|
Satellite two-line elements (TLEs) is a standard data used to compute satellite |
 |
The Hipparcos-Tycho Catalog is the primary stellar databases used to display information by TheSky for stars to about 12 magnitude and brighter. TheSky also cross-references stars from the following catalogs:
|
Catalog Cross References
TheSky cross-references the following catalogs. Use TheSky's powerful Edit > Find feature to locate them.
|
Cross-Referenced Catalogs |
Search Prefix |
Object Count |
| Arakelian Catalog of Galaxies | ARAK |
595 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed Designations | n/a |
n/a |
| Bonner Durchmusterung Number | B+nn nnnnn |
- |
| Caldwell Catalog | Caldwell + Cn |
109 |
| Cape Durchmusterung Number | P-nn nnnn |
- |
| Catalog of Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies | CGCG |
29,809 |
| Common Non-Stellar Object Names | name of object |
|
| Common Star Names | name of object |
|
| Constellations | name of constellation |
88 |
| Cordoba Durchmusterung | C-nn nnnnn |
- |
| David Dunlop Observatory Catalog of Galaxies | DDO |
242 |
| Fairall Catalog of Galaxies | FAIR |
1,185 |
| Henry Draper number | HD |
359,083 |
| Infrared Astronomical Survey | IRAS |
9,347 |
| Karachentseva Catalog of Galaxies | KARA |
183 |
| Kazaryan UV Galaxies | KAZ |
581 |
| Kiso UV Galaxies | KUG |
5,455 |
| Messier Catalog | M |
110 |
| Positions and Proper Motions Number | PPM |
- |
| Second Byurakay Survey | SBS |
259 |
| Smithsonian Astrophysical Catalog (SAO) | SAO |
258,997 |
| Struve Catalog | STRUVE |
3,100 |
| Tololo Galaxies | TOL |
111 |
| University of Michigan Catalog of Galaxies | UM |
652 |
| unnamed | 1SZ |
26 |
| unnamed | 2SZ |
32 |
| unnamed | ARP |
560 |
| unnamed | ESO |
16,239 |
| unnamed | LGS |
5 |
| unnamed | VV |
1,161 |
| Uppsala General Catalog of Galaxies | UGC |
13,073 |
| Virgo Cluster Catalog of Galaxies | VCC |
2097 |
| Weinberger Catalog of Galaxies | WEIN |
207 |
| Zwicky1 | 1ZW |
238 |
| Zwicky2 | 2ZW |
199 |
| Zwicky3 | 3ZW |
159 |
| Zwicky4 | 4ZW |
203 |
| Zwicky5 | 5ZW |
531 |
| Zwicky6 | 6ZW |
238 |
| Zwicky7 | 7ZW |
1,145 |
| Zwicky8 | 8ZW |
645 |
Optional Sky Databases (SDBs)
TheSky includes additional astronomical catalogs as optional Sky
Databases.
|
Optional Sky Databases |
Search Prefix |
Object Count |
Object Type |
|
1.4-GHz Northern Sky |
1-4ghz |
31524 |
Reference Point |
|
6C Survey of Radio Sources |
6CSRSI |
1761 |
Radio Source |
|
6C Survey of Radio Sources II |
6CSRSII |
8278 |
Radio Source |
|
6C Survey of Radio Sources III |
6CSRSIII |
8749 |
Radio Source |
|
6C Survey of Radio Sources IV |
6CSRS-IV |
5421 |
Radio Source |
|
6C Survey of Radio Sources V – A |
6CSRS-VA |
2229 |
Radio Source |
|
6C Survey of Radio Sources V – B |
6CSRS-VB |
1229 |
Radio Source |
|
6C Survey of Radio Sources VI |
6CSRS-VI |
6752 |
Radio Source |
|
Abell - Zwicky Clusters of Galaxies |
AGC |
2712 |
Cluster of Galaxies |
|
Abell Planetary Nebulae |
APN |
86 |
Nebula |
|
Ackerman Red Stars |
ARS |
267 |
Reference Point |
|
APM Bright Galaxy Catalogue |
APM |
14681 |
Galaxy |
|
Arp Globular Clusters |
Arp-GC |
43 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Arp Peculiar Galaxies |
ARP-PG |
38 |
Galaxy |
|
Barnard's Dark Nebulae |
Barnard |
349 |
Dark Nebula |
|
Bright Nebulae Drawings (TMB) |
TMB-BN |
25743 |
Bright Nebula |
|
Catalog of Bright Galaxies |
CBG |
4364 |
Galaxy |
|
Celestron NexStar Doubles |
CND |
55 |
Double Star |
|
Cepheids in the Large Magellanic Cloud |
LMC-CV |
97 |
Variable Star |
|
Cluster System of the Large Magellanic Cloud |
LMC-CL |
1762 |
Mixed Deep Sky |
|
Cool Galactic Carbon Stars |
CCS |
5987 |
Reference Point |
|
Cousins Photometric Standards |
CPS |
670 |
Reference Point |
|
Culled Henden CI Labels |
HC-L |
0 |
Reference Point |
|
Dark Nebulae Isophotes TMB |
DND |
650 |
Dark Nebula |
|
Declination Zero |
51 |
Reference Line |
|
|
Declination Zero Label |
|
13 |
Reference Point |
|
DeepMap 600 |
|
470 |
Reference Point |
|
Don Macholtz Messier Marathon |
Macholtz |
110 |
Target Object |
|
Double Stars with common names |
|
169 |
Double Star |
|
Einstein Observatory Ex M-S Survey |
EMSS |
835 |
X-Ray Source |
|
Feitzinger Dark Nebula |
FZ-DN |
489 |
Dark Nebula |
|
Feitzinger Globules |
FG |
331 |
Reference Point |
|
Florsch - Small Magellanic Cloud Stars |
SMC-Florsch |
584 |
Reference Point |
|
G2 V Stars from SIMBAD Query |
G2V |
688 |
Reference Point |
|
Galactic Globular Clusters – Monella |
GC-Monella |
160 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Galactiglob Galaxies |
TJ-GG |
2495 |
Galaxy |
|
Galaxy Isophote M51 Example |
BSR-GI |
902 |
Galaxy |
|
Heinz Nebula Small Magellanic Cloud |
HN |
117 |
Nebula |
|
Hendon 3C |
H3C |
504 |
Reference Point |
|
Herbig-Haro Objects |
HH |
454 |
Reference Point |
|
HW Clusters Large Magellanic Cloud |
HW-SMC |
87 |
Globular Cluster |
|
IRAS 1.2 Jy Redshift |
IRAS-1.2 |
9899 |
Galaxy |
|
IRAS Small Scale Structure |
IRASS |
16740 |
Reference Point |
|
Kron Clusters Small Magellanic Cloud |
SMC-KRON |
69 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Landolt Faint Photometric Standards |
LFPS |
526 |
Reference Point |
|
Landolt Photometric Standards |
LPS |
1154 |
Reference Point |
|
Landolt Photometric Standards South |
LPS-S |
109 |
Reference Point |
|
Lindsay Clusters Small Magellanic Cloud |
SMC-L |
118 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Lynds' Bright Nebulae |
LBN |
1053 |
Bright Nebula |
|
Lynds' Dark Nebulae |
LDN |
1791 |
Dark Nebula |
|
Meade Alignment Star Labels |
MAS |
78 |
Reference Point |
|
Michael Covington Deep Sky Objects |
COV |
200 |
Mixed Deep Sky |
|
Milky Way Globular Clusters |
MW-GC |
150 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Molonglo Reference - Radio Sources |
Molongo Radio |
12141 |
Radio Source |
|
Navigational Stars |
NavStar |
58 |
Reference Point |
|
NB Carbon Stars – Skiff |
NBC |
211 |
Reference Point |
|
Nebulae in the Magellanic Clouds- HII |
LMC-HII |
358 |
Nebula |
|
NGC and IC objects UNKNOWN magnitudes |
|
982 |
Mixed Deep Sky |
|
NGC Max Alignment Stars – JMI |
JMI |
30 |
Star |
|
Objects in the Direction of the SMC |
SMC-B |
965 |
Reference Point |
|
Open Cluster Data 5th Edition (Lynga 1987) |
OC-L |
1151 |
Open Cluster |
|
Palomar Globular Clusters |
PAL |
15 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Palomar Sky Survey - 102 CD labels |
DSS-102 |
0 |
Reference Point |
|
Palomar Sky Survey Plates Additional Data |
POSS |
1037 |
Reference Point |
|
Parkes Radio Sources |
PKS90 |
8264 |
Radio Source |
|
Planetary Nebulae in LMC |
LMC-PLN |
169 |
Planetary Nebula |
|
Pulsars (Taylor+1993) |
PULSARS |
558 |
Radio Source |
|
Query Common Non-Stellar |
|
329 |
Mixed Deep Sky |
|
RealSky CD's North Labels |
RealSky-N |
765 |
Reference Point |
|
RealSky CD's South Labels |
RealSky-S |
800 |
Reference Point |
|
RealSky North & South Labels |
RealSky-NS |
658 |
Reference Point |
|
Redshift Galaxies |
RG |
12844 |
Galaxy |
|
Rich Clusters of Galaxies (North) |
RC-GN |
2712 |
Cluster of Galaxies |
|
Rich Clusters of Galaxies (South) |
RC-GS |
1364 |
Cluster of Galaxies |
|
Roslund Red Stars in Scorpious |
RR |
69 |
Reference Point |
|
Seyfert Galaxies |
Seyfert |
121 |
Galaxy |
|
Shapley-Ames Bright Galaxies |
SA-BG |
1246 |
Galaxy |
|
Shapley-Ames Bright Galaxies |
SA-BG |
1246 |
Galaxy |
|
Sharpless HII Regions |
SH- |
313 |
Nebula |
|
Skiff North Bright Standards |
BK-NBS |
119 |
Reference Point |
|
Star Clusters and Associations |
SCA |
1039 |
Open Cluster |
|
Stars in the Double-Double |
DDS |
2 |
Star |
|
Supernova Remnants – Green |
SNR-G |
231 |
Supernova |
|
Terzan Globular Clusters |
Ter |
11 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Third Catalogue of Nearby Stars |
CNS3 |
3802 |
Reference Point |
|
Trapezium Circumstellar disks |
TCD |
149 |
Reference Point |
|
Trapezium ROSAT PSPC |
Trap-XRay |
171 |
X-Ray Source |
|
Trapezium Stars – TMB |
|
14 |
Star |
|
Trapezium Stars VizieR |
Trap-Vzr |
292 |
Reference Point |
|
Trumpler Clusters |
Tr |
34 |
Open Cluster |
|
Trumpler Stars |
Tr-S |
39 |
Reference Point |
|
UV-Excess Galaxies |
UVG |
8162 |
Galaxy |
|
Van Den Berg Reflection Nebulae |
Vdb |
158 |
Nebula |
|
Video Calibration Stars |
VCS |
958 |
Target Object |
|
W-G Clusters Small Magellanic Cloud |
WG |
18 |
Globular Cluster |
|
Yale Bright Star Catalog 1st half |
YBSC-1 |
4991 |
Star |
|
Yale Bright Star Catalog 2nd half |
YBSC-2 |
4105 |
Star |
Want More Data?
There are literally millions of astronomical catalogs, and TheSky does not include them all. If TheSky's supplied databases of objects are not enough, and you wish to access a database that is not currently included, please let us know, and we'll try to add your database to future updates, or post it for download.
Ephemeral Data
TheSky predicts and charts the positions of comets, minor planets, and artificial satellites. The data required to accurately display these objects changes frequently and must be updated from different sources on the web. Use the links below to download updated orbital element data. TheSky can be configured to automatically download TLE datasets each time it is launched.
Use TheSky's Edit > Find command to locate any object from these catalogs.
|
Object Type |
Object Count |
Web Site Address to Obtain Updated Orbital Element Data |
|
Comets |
Up to 1100 at a time |
Minor Planet Center: https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/iau/Ephemerides/Soft06.html
|
|
Artificial Satellites |
Up to 20,000 at a time |
Celestrak Web Site: http://celestrak.com/
|
|
Large Database Asteroids |
All known asteroids |
There are presently more than 1 million know asteroids and more being discovered Minor Planet Center: https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/iau/MPCORB.html Lowell Observatory: http://asteroid.lowell.edu |
My Chart Elements
TheSky Professional allows you to add objects to the Sky Chart (such as stars, galaxies, labels or reference lines and more) so that you can generate your own databases.
Photographs
TheSky Professional includes photos of many deep-space objects, planets, the Moon and more.
-
Over 13,000 monochrome photos from the NGC and IC Catalogs.
-
Over 95,000 Digitized Sky Survey thumbnail photos PGC Catalog galaxies.
-
Photos of every object in the Messier catalog.
-
Photos of solar system objects, including images from the Mars Rover and other space missions.
-
Over 1000 high-resolution photographs of the Moon that can be labeled by crater (name and size).
-
Miscellaneous comet, asteroid, and Apollo mission photos.
Device Control
TheSky has extensive features to operate your astrophotography equipment.
Telescope Control
 |
The table below lists the "go to" and "push to" telescope models supported by TheSky Professional. For step-by-step setup instructions on how to setup and control telescopes with TheSky, see Telescope Control in TheSky Professional and Serious Astronomer User Guide. |
Telescope Control Features
TheSky Astronomy Software was first used to direct and control telescopes back in 1988. Since then, we've enhanced and refined the user interface based on feedback from thousands of passionate astronomers. The result is a friendly, easy-to-use interface, packed with a powerful feature set.
|
Connect |
Center Cross Hairs |
Add Telrad™ Finder to Sky Chart |
Stop |
|
Telescope |
Star Synchronization |
Spiral Search |
Park mount |
TheSky's telescope-related controls documentation is here.
***
Natively Supported Telescopes and Robotic Telescope Mounts
TheSky Professional controls the following mounts.
|
Manufacturer |
Series |
Model |
|
|
|
||
| GTO series mounts | All models1 , including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Advanced Series | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Advanced VX Mounts | All models |
|
|
|
|
||
| CGEM Series | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| CGE Series | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| CPC Series | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| GT Series | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| NexStar GPS | All models, including
|
|
|
|
|
||
| i Series | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| NexStar (non-GPS) | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| SE Series | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Sky Prodigy Series | All models |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Ultima |
*Software Bisque considers the Celestron Ultima 2000 telescope a "legacy" product as relatively few of these telescopes are still in use.While TheSky includes a driver for the Ultima 2000, we no longer provide technical support when using TheSky to control this mount. |
||||||
| SmartStar Az/Alt "Cube" mount with GotoNova Controller |
All models*
See TheSky To date, iOptron has released three
* Earlier model Optron SmartStar mounts used the Silicon Labs CP210X USB to UART Bridge for serial communications on macOS and Windows. This UART requires a Virtual Serial Port Driver to be installed before TheSky can communicate with these model mounts. The CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP Drivers (VCP Driver Kit) are available from the Silicon Labs web site. Note that iOptron mounts using the serial command protocol version 2 and later do not require installation of a VCP driver. ** |
|
|
|
|
||
| German Equatorial Mounts |
All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| NGC Sky Vector and Sky Commander |
All models |
|
|
|
|
||
| MI Series Mounts | All modes, including:
Mathis Instruments mounts use either the Gemini Astronomical Positioning System or the Bisque TCS (TheSky Professional only). |
|
|
|
|
||
| LX200™ (classic) | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Autostar | All models, including:
*Requires Meade Autostar Computer Controller #497 with RS232 serial port. |
|
|
|
|
||
| LX200 GPS Series (Autostar II) |
All models, including:
ACF Models
SCTs
"Ritchey-Chrétian"
|
|
|
|
|
||
| MI-250 Equatorial Mounts |
Mountain Instruments mounts use Gemini Astronomical Positioning System for go to telescope control. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Orion®
|
Atlas™ EQ-G Equatorial |
This mount uses the same control system (and the same serial communication protocol) as the NexStar GPS and other later model Celestron International "go to" telescopes. |
|
|
|
|
|
| Sirius™ EQ-G Equatorial Mounts |
This mount uses the same control system (and the same serial communication protocol) as the NexStar GPS and other later model Celestron International "go to" telescopes. |
|
|
|
|
||
| SkyQuest IntelliScope
|
See Tangent Instruments Device Support below |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
All models |
|
|
|
|
||
| Gemini Astronomical Positioning System |
All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Sky Commander | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sky-Watcher™ Mounts |
All models that use the SynScan Controller, including:
The SkyWatcher mounts use the SynScan control system for go See USB Adapters for more information about physically connecting |
|
|
|
|
|
| BBox | Software Bisque's BBox (manufactured by Tangent Instruments) that started the "push to telescope" revolution. |
|
|
|
|
||
| Paramount ME Robotic Telescope Mount |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Paramount Robotic Telescope Mounts |
All models, including: |
|
|
|
|
||
| All models |
|
|
|
|
|||
| Temma | All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Encoder-to-serial boxes |
All models, including:
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Sky Sensor | All models |
|
|
|
|
||
|
STAR |
TheSky Professional can control any mount that uses the STAR BOOK Star-Chart Go To System, including (but not limited to) the following models:
If your specific telescope model is not listed, but uses the |
|
|
|
|
||
| Argo Navis | All models |
|
|
|
|
1 TheSky
Professionals native Astro-Physics mount driver states that firmware version
G or later is required to control Astro-Physics compatible telescopes.
Note that if you own an older model AP controller that uses an earlier
firmware version, TheSky Professional will still control it; however,
newer firmware features will not be available.
Software Bisque strongly recommends using the latest available
firmware for your telescope. Contact Astro-Physics for details
about upgrading your mount's firmware.
X2 Plug In-Compatible Mount Control
TheSky Pro's X2 Standard
lets third-party developers add support for new or previously-unsupported
devices. TheSky Professional can control the following telescopes
by installing a X2 Telescope Plug In:
|
Device |
Model |
|
|
|
|
| AstroTrac 360 GEM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Astrometric Instruments' |
Mounts using the Astrometric Instruments Telescope Control System |
|
|
|
|
|
iOptron™ Mounts
|
CEM120xx model mounts |
|
|
|
|
|
Gemini Telescope |
Mounts using the Pulsar GoTo controller |
|
|
|
|
|
Sky-Watcher™ |
EQ6, HEQ5, EQ5, EQ3, EQ8, and the AZEQ5 and AZEQ6 in EQ mode only. |
|
|
|
|
2An open-source
X2 Mount Plug In for these model mounts can be downloaded
and installed separately from the RTI-Zone
web page.
Non-Natively Supported
Telescope Mounts
TheSky supports the following third-party driver models for telescope
control.
|
Driver |
Model |
|
|
|
|
|
ASCOM (Windows only) |
TheSky Professional for Windows can control any telescope mount that has an ASCOM-compatible driver. The Windows-only ASCOM platform and the Windows-only ASCOM-specific telescope driver must be downloaded and installed separately. |
- |
|
- |
- |
USB Adapters
Many commercial telescope mounts communicate with the personal computer
using RS-232
serial communication. In order to communicate with modern computers
that no longer include RS-232 DB-9 serial ports, a USB
adapter is required. FTDI-based USB adapters, like this
one, are compatible with most operating systems and do not require
installation of a software driver.